What Is the Prostate Gland?
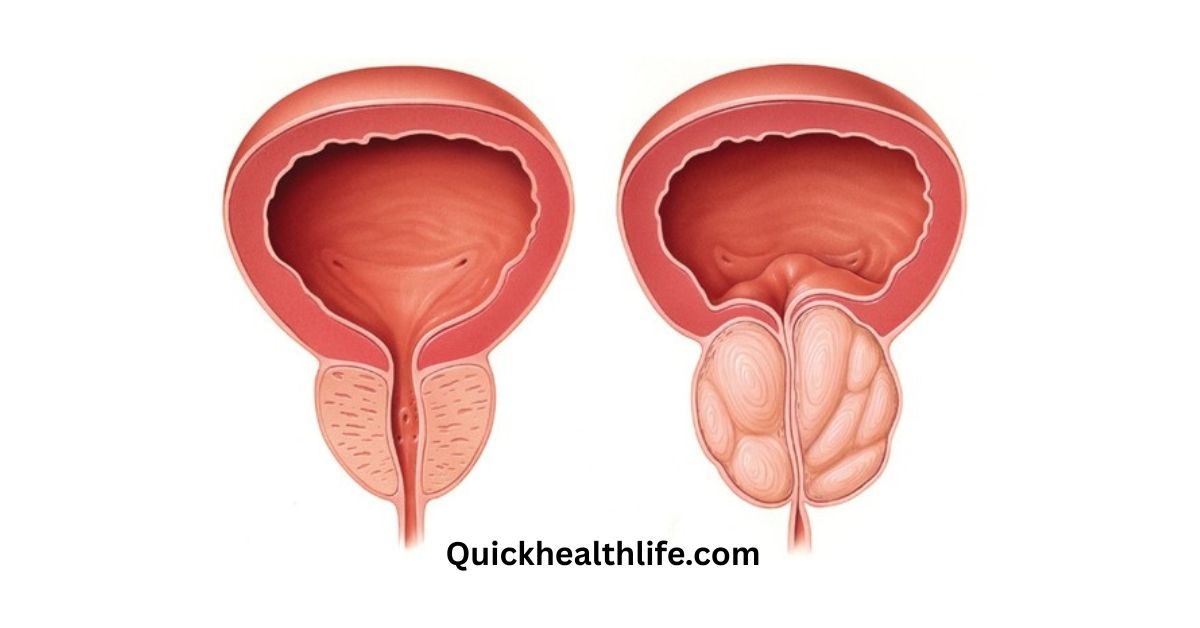
The prostate gland is a small walnut-shaped organ found below the bladder in men. It surrounds the urethra — the tube that carries urine and semen out of the body. The prostate’s main role is to produce a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
Table of Contents
Role and Function of the Prostate
The prostate plays a crucial role in male fertility and urinary control. Its main functions include:
- Producing seminal fluid, which mixes with sperm during ejaculation.
- Helping control urine flow by contracting and relaxing its muscles.
- Supporting healthy sperm by providing a nutrient-rich environment.
A healthy prostate ensures normal reproductive and urinary function. However, when it becomes enlarged or inflamed, it can cause severe discomfort and urinary issues.
Common Prostate Problems
There are three major types of prostate disorders that men may face during their lifetime:
1. Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH, also known as an enlarged prostate, is a non-cancerous condition that commonly affects older men. The enlarged gland presses against the urethra, causing urination difficulties.
Symptoms include:
- Frequent urination at night
- Weak urine flow
- Difficulty starting or stopping urination
2. Prostatitis
Prostatitis refers to the inflammation of the prostate caused by infection or injury. It can affect men of all ages.
Key signs:
- Pelvic pain
- Burning sensation during urination
- Fever and fatigue
3. Prostate Cancer
This is one of the most common cancers among men worldwide. It occurs when cells in the prostate start growing uncontrollably.
Early detection is critical, as prostate cancer often shows no symptoms in the early stages. Regular PSA tests are highly recommended after age 50.
Symptoms of Prostate Problems
Many men ignore early prostate symptoms, assuming they’re just part of aging. But recognizing them early helps prevent complications.
Common warning signs include:
- Difficulty urinating
- Pain in the lower back or pelvis
- Blood in urine or semen
- Weak urine stream
- Painful ejaculation
- Frequent urge to urinate, especially at night
If you’re wondering, “How did I know I had a prostate issue?”, it often starts with small urinary changes that gradually worsen.
Causes and Risk Factors
The causes of prostate problems vary depending on the condition, but some common factors include:
| Risk Factor | Description |
|---|---|
| Age | Most prostate issues occur after age 50 |
| Hormonal changes | Testosterone and DHT imbalances |
| Diet | High-fat diets increase the risk |
| Genetics | Family history of prostate cancer |
| Infection | Bacterial infections can cause prostatitis |
| Lifestyle | Smoking, stress, and lack of exercise |
Types of Prostate Disorders
- Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH) – Non-cancerous enlargement
- Prostatitis – Inflammatory condition
- Prostate Cancer – Malignant growth
Each type needs a different approach for diagnosis and treatment, which we’ll explore below.
Diagnosis: How Prostate Issues Are Detected?
Doctors use a combination of tests to diagnose prostate problems:
1. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
A quick physical test to check for enlargement or abnormalities.
2. Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Test
A blood test that measures PSA levels — high levels may indicate cancer or inflammation.
3. Imaging & Biopsy
MRI, ultrasound, or tissue biopsy confirm the presence and type of prostate disorder.
Treatment
The right treatment depends on the diagnosis. Here are common solutions:
1. Medications
- Alpha-blockers (like Tamsulosin) relax prostate muscles.
- Antibiotics treat bacterial prostatitis.
- Hormone therapy reduces testosterone in prostate cancer cases.
2. Natural Remedies & Lifestyle Changes
- Eat tomatoes, green tea, and pumpkin seeds for prostate health.
- Exercise regularly to improve blood flow.
- Avoid caffeine and alcohol.
3. Surgical Options
For severe cases, surgeries like TURP (Transurethral Resection of the Prostate) or laser therapy may be recommended.
Complications If Left Untreated
Ignoring prostate problems can lead to:
- Urinary retention (inability to urinate)
- Bladder damage
- Kidney failure
- Sexual dysfunction
- Spread of cancer (if malignant)
How to Maintain a Healthy Prostate
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay hydrated and limit alcohol.
- Exercise regularly to maintain hormonal balance.
- Get routine checkups, especially after age 45.
Tip: To clean your prostate naturally, consume foods rich in antioxidants and zinc — such as nuts, berries, and spinach.
FAQs About Prostate Health
1. What does the prostate do for a man?
It produces seminal fluid that nourishes and protects sperm.
2. What are the symptoms of a prostate problem?
Difficulty urinating, pain in the pelvis, and blood in urine are common signs.
3. How to clean your prostate naturally?
Drink plenty of water, eat tomatoes, and include omega-3 fats in your diet.
4. Is prostate cancer curable?
Yes, if detected early, prostate cancer is highly treatable.
5. What is the best prostate medication?
Alpha-blockers and 5-alpha-reductase inhibitors are common options.
6. How can I prevent prostate problems?
Maintain a healthy lifestyle, avoid smoking, and get regular prostate screenings.