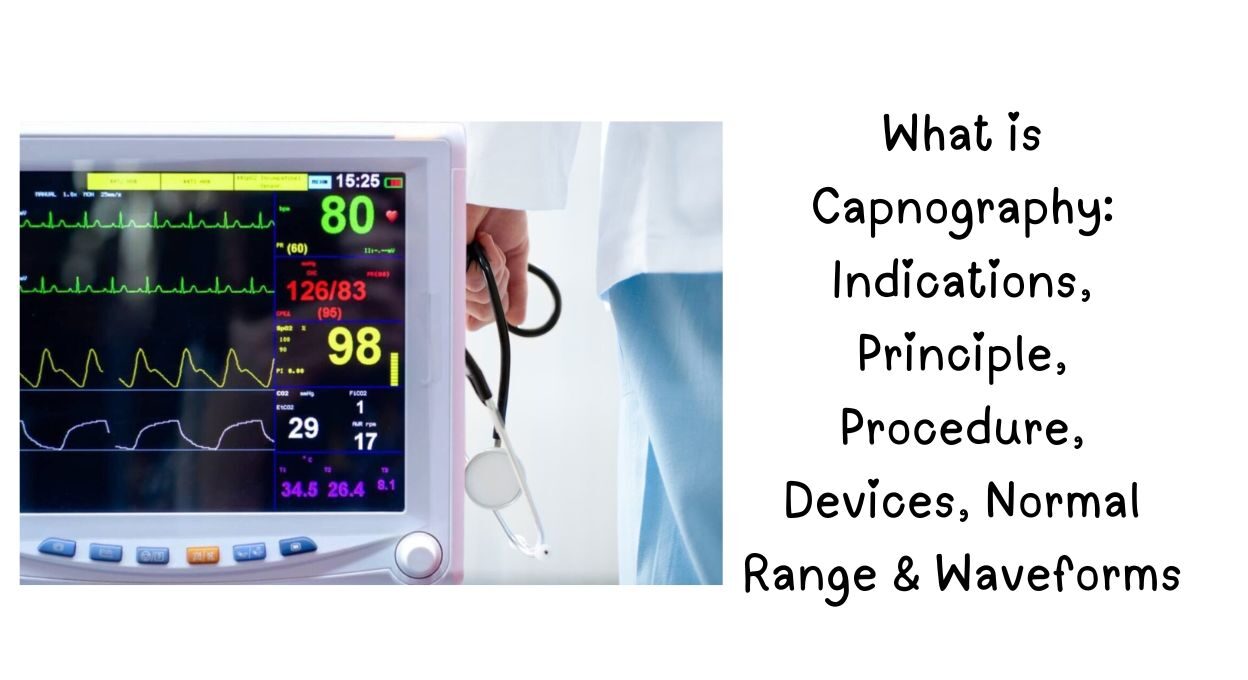
Capnography is a non-invasive, real-time monitoring tool that measures end-tidal carbon dioxide (EtCO₂) in exhaled breath. It is widely used in:
✔ Anesthesia (to prevent hypoventilation)
✔ Emergency medicine (for confirming tube placement)
✔ Critical care (ventilator management)
✔ EMS (prehospital monitoring)
Why is capnography crucial?
- Detects respiratory depression before oxygen levels drop.
- Confirms proper endotracheal intubation.
- Monitors cardiac output during CPR.
Table of Contents
What is Capnography?
Definition & Purpose
Capnography tracks CO₂ concentration during breathing cycles, helping assess:
- Ventilation efficiency
- Metabolic activity
- Airway integrity
Capnography in Modern Healthcare
- Operating Rooms: Prevents anesthesia-related complications.
- ICUs: Monitors mechanically ventilated patients.
- Emergency Departments: Ensures correct airway management.
Capnography Principle
Infrared Absorption Spectroscopy
CO₂ absorbs infrared light at a specific wavelength (4.26 µm). The device calculates CO₂ levels based on absorption.
Types of Capnography Systems
| Type | How It Works | Pros & Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Mainstream | Sensor in airway | ✔ Fast response ❌ Bulky |
| Sidestream | Samples gas via tube | ✔ Lightweight ❌ Delayed readings |
Capnography Indications
Critical Care Uses
- Ventilator adjustments
- Detecting pulmonary embolism (sudden EtCO₂ drop)
Emergency Applications
- Tube placement verification
- ROSC detection in CPR (rising EtCO₂ = effective compressions)
Capnography Monitor
✔ Real-time EtCO₂ values (35–45 mmHg = normal)
✔ Waveform display (identifies obstructions)
✔ Alarms for apnea/hypoventilation
Capnography Procedure
- Connect sensor to the airway circuit.
- Calibrate (if required).
- Monitor continuously for changes.
Safety Tips:
- Avoid moisture in sidestream tubing.
- Check for leaks.
Capnography Normal Range & Interpretation
| EtCO₂ Value | Interpretation |
|---|---|
| 35–45 mmHg | Normal |
| < 35 mmHg | Hyperventilation, low cardiac output |
| > 45 mmHg | Hypoventilation, CO₂ retention |
Capnography Devices
Portable (EMS/Field Use)
- Philips Capnostream 20
- Masimo Rad-97
Advanced Hospital Devices
- GE Healthcare CARESCAPE
- Draeger Infinity® M540
Capnography Waveforms
Normal Waveform Phases
- Phase I (Baseline) – Dead space gas
- Phase II (Rising slope) – Alveolar gas mixing
- Phase III (Alveolar plateau) – Exhalation
- Phase 0 (Inhalation) – CO₂ drops
Abnormal Waveforms
- Shark fin = Bronchospasm
- Curare cleft = Partial paralysis
Capnography PPT & Training Resources
- Free downloadable PPTs (Google Scholar, medical universities)
- Simulation training tools (e.g., CAE Healthcare)
Advantages & Limitations
✅ Pros:
- Early warning for respiratory failure
- Non-invasive
❌ Cons:
- Requires training for interpretation
- Sidestream delays in high humidity
FAQs About Capnography
1. What is the normal range for capnography?
Answer: 35–45 mmHg (end-tidal CO₂).
2. Can capnography detect cardiac arrest?
Answer: Yes, low EtCO₂ (< 10 mmHg) suggests poor circulation.
3. Mainstream vs. sidestream capnography?
Answer: Mainstream is faster; sidestream is lighter.
4. How often should capnography be calibrated?
Answer: Follow manufacturer guidelines (often pre-use).
5. Why is capnography used in sedation?
Answer: Prevents undetected hypoventilation.