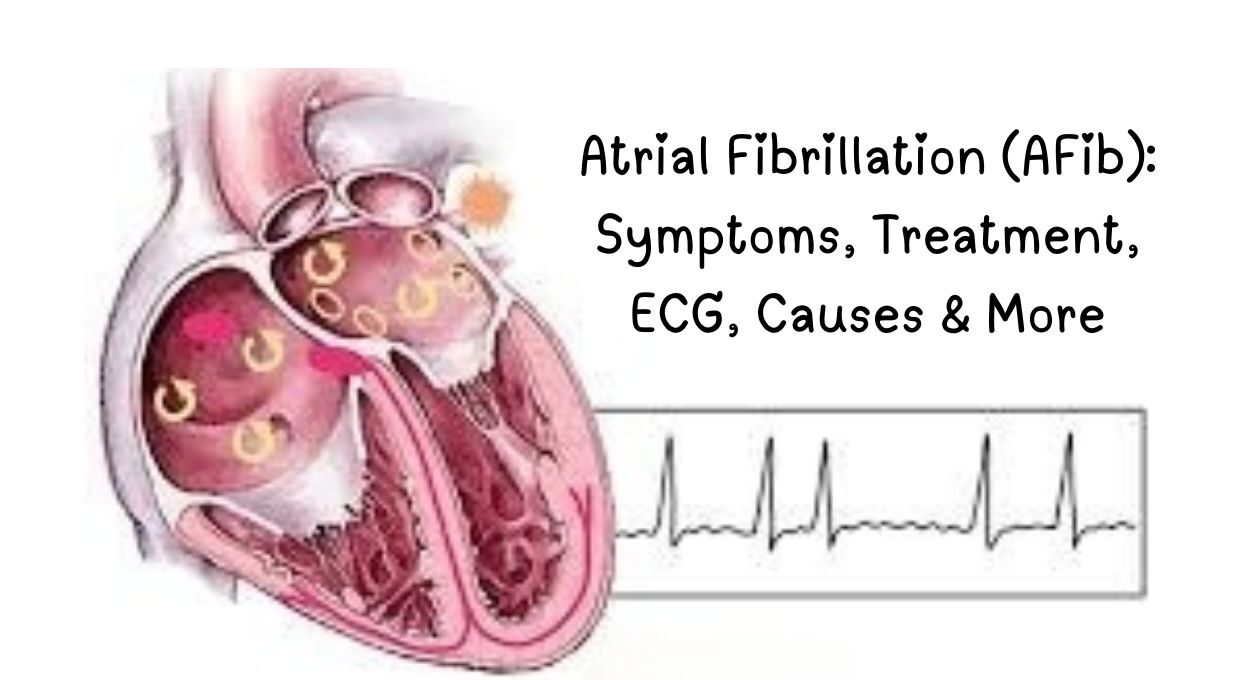
What is Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)?
Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is an irregular and often rapid heart rhythm originating in the atria (upper heart chambers). It affects over 33 million people worldwide and increases stroke risk by 5x.
✔ Most common sustained arrhythmia
✔ Can be paroxysmal (comes and goes) or persistent
✔ Not always life-threatening but requires treatment
Table of Contents
4 Types of Atrial Fibrillation (AFib)
Atrial fibrillation is classified based on how long episodes last and how they respond to treatment. Understanding your type helps guide management.
1. Paroxysmal Atrial Fibrillation
- Definition: Comes and goes, lasting <7 days (usually <24 hrs)
- Key Features:
✔ Episodes stop on their own
✔ May feel palpitations or no symptoms
✔ Can progress to persistent AFib - Special Case: When alternating with slow heart rate = Tachy-Brady Syndrome
2. Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- Definition: Lasts >7 days, won’t stop without treatment
- Key Features:
✔ Requires cardioversion or meds to reset rhythm
✔ Higher stroke risk than paroxysmal
✔ Often needs long-term blood thinners
3. Long-Term Persistent Atrial Fibrillation
- Definition: Continuous AFib for >1 year
- Key Features:
✔ Harder to treat
✔ Ablation may still help
✔ Focus shifts to rate control vs rhythm control
4. Permanent Atrial Fibrillation
- Definition: Ongoing AFib where restoring normal rhythm is no longer attempted
- Key Features:
✔ Patient and doctor decide to stop trying to convert rhythm
✔ Treatment focuses on:- Rate control (beta blockers)
- Stroke prevention (blood thinners)
- Managing symptoms
Atrial Fibrillation Symptoms
Symptoms vary—some people feel nothing (silent AFib), while others experience:
✅ Palpitations (fluttering heartbeat)
✅ Fatigue & dizziness
✅ Shortness of breath
✅ Chest pain (seek emergency care!)
✅ Fainting (syncope)
When to See a Doctor:
- If your heartbeat feels irregular
- If you have chest pain + dizziness
Atrial Fibrillation ECG: How It’s Diagnosed
Classic AFib ECG Signs
| Feature | Normal ECG | AFib ECG |
|---|---|---|
| P-Waves | Present | Absent (irregular “fibrillary waves”) |
| Heart Rate | 60-100 bpm | Often 100-175 bpm |
| Rhythm | Regular | Irregularly irregular |
Other Tests:
- Holter monitor (24-48 hr ECG)
- Echocardiogram (checks for structural issues)
What Causes Atrial Fibrillation?
Top 7 Causes of AFib
- High blood pressure (#1 risk factor)
- Heart disease (CAD, valve problems)
- Age (over 65 highest risk)
- Obesity & sleep apnea
- Alcohol & caffeine excess
- Hyperthyroidism
- Family history
Atrial Fibrillation vs. Atrial Flutter
| Feature | Atrial Fibrillation (AFib) | Atrial Flutter |
|---|---|---|
| Heart Rhythm | Chaotic, irregular | Organized, sawtooth pattern |
| ECG Pattern | No P-waves, erratic | Flutter waves (F-waves) |
| Heart Rate | Very irregular | Often steady 150 bpm |
| Treatment | Blood thinners, ablation | Similar but easier to control |
Atrial Fibrillation Treatment
1. Medications
| Drug Type | Purpose | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Rate Control | Slows heart rate | Metoprolol, Diltiazem |
| Rhythm Control | Restores normal rhythm | Amiodarone, Flecainide |
| Blood Thinners | Prevents stroke | Warfarin, Eliquis, Xarelto |
2. Procedures
- Cardioversion (electric shock to reset rhythm)
- Ablation (burns abnormal heart tissue)
- Left Atrial Appendage Closure (Watchman device)
3. Lifestyle Changes
✔ Limit alcohol & caffeine
✔ Exercise moderately
✔ Eat a heart-healthy diet
How Atrial Fibrillation Damages Your Health
1. Blood Clots & Stroke (Most Dangerous Complication)
- Why it happens: Chaotic heart rhythm lets blood pool and clot
- Key stats:
✔ AFib increases stroke risk 5-fold
✔ 25% of strokes in elderly are AFib-related
✔ Black patients have 38% higher stroke rates than white patients with AFib
Warning signs of stroke (FAST):
- Face drooping
- Arm weakness
- Speech difficulty
- Time to call 911
2. Heart Failure
- Mechanism: Irregular beats weaken heart muscle over time
- Symptoms:
✔ Shortness of breath
✔ Swelling in legs
✔ Extreme fatigue
3. Cognitive Decline & Dementia
- 2X higher risk of Alzheimer’s and vascular dementia
- Causes:
✔ Silent mini-strokes
✔ Reduced blood flow to brain
4. Racial Disparities in AFib Outcomes
| Complication | Black Patients | White Patients |
|---|---|---|
| Stroke risk | 38% higher | Baseline |
| Heart failure | 53% more likely | Baseline |
| Mortality | 22% higher | Baseline |
(Source: American Heart Association 2023 Report)
Critical Prevention Strategies
Medical Treatments
- Blood thinners: Warfarin or DOACs (Eliquis/Xarelto)
- Rate control: Beta blockers, calcium channel blockers
- Rhythm control: Cardioversion, ablation
Lifestyle Modifications
✔ Weight management (Lose 10% weight → 50% fewer AFib episodes)
✔ Alcohol reduction (Even 1 drink/day increases risk)
✔ Sleep apnea treatment (CPAP cuts AFib recurrence by 42%)
Monitoring & Emergency Preparedness
When to Seek Immediate Help
| Symptom | Possible Complication |
|---|---|
| Sudden numbness | Stroke |
| Coughing blood | Internal bleeding |
| Chest pressure | Heart attack |
| Fainting + no pulse | Cardiac arrest |
Routine Care Checklist
- Weekly INR checks if on warfarin
- Annual echocardiogram
- Monthly symptom diary
Can Atrial Fibrillation Be Cured?
- Some patients can be cured with ablation.
- Others need lifelong medication to manage symptoms.
- Early treatment improves outcomes.
Atrial Fibrillation Life Expectancy
- With proper treatment, most live a near-normal lifespan.
- Untreated AFib increases stroke & heart failure risk.
- Key factor: Controlling underlying conditions (e.g., hypertension).
Atrial Fibrillation ICD-10 Code
- ICD-10 Code: I48.91 (Unspecified AFib)
- Used for medical billing & records.
FAQ About Atrial fibrillation?
1. What is the main cause of atrial fibrillation?
Answer: High blood pressure is the leading cause, but aging, heart disease, and lifestyle factors also contribute.
2. Can you live a long life with atrial fibrillation?
Answer: Yes, with proper treatment (blood thinners, rate control), most patients have a normal lifespan.
3. Does AFib show on an ECG?
Answer: Yes, an ECG shows irregular rhythm, absent P-waves, and fast heart rate.
4. What’s the difference between AFib and atrial flutter?
Answer: AFib is chaotic & irregular, while flutter has a sawtooth ECG pattern.
5. Is atrial fibrillation curable?
Answer: Sometimes—ablation can cure it, but many need ongoing medication.