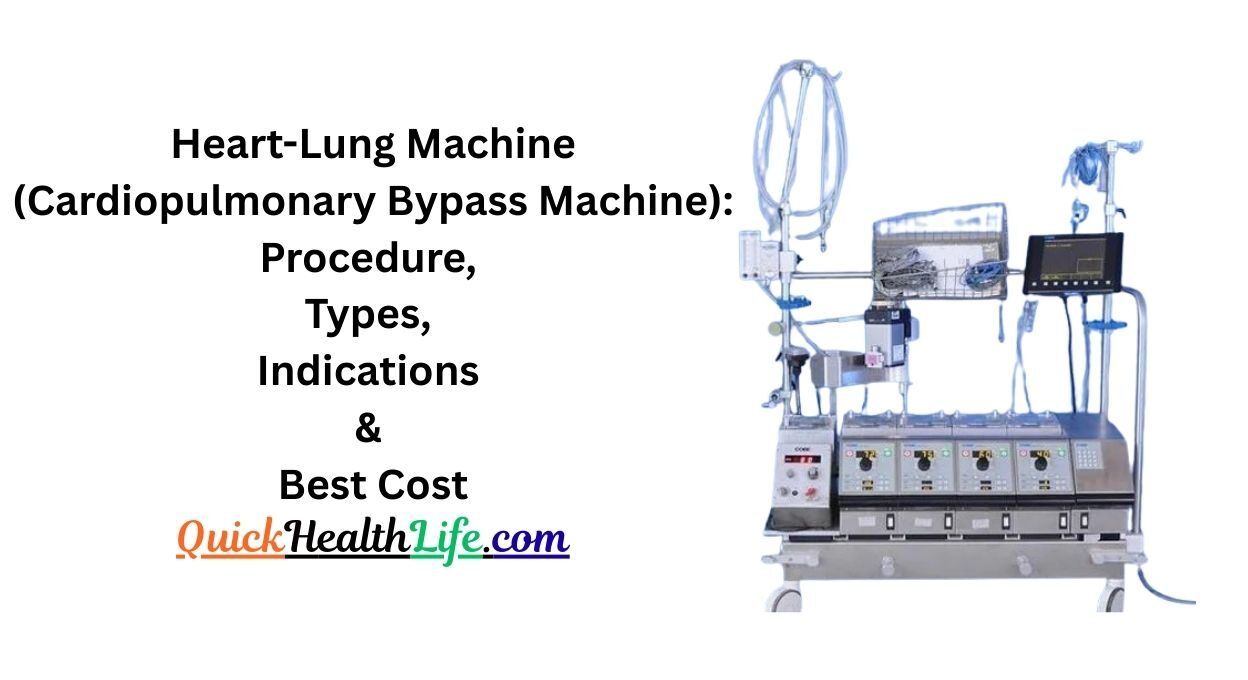
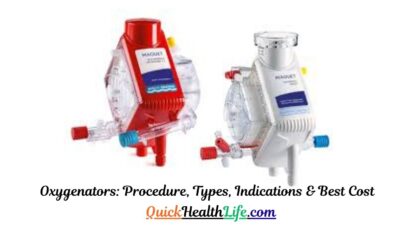
The heart-lung machine, also called the cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB) machine, is one of the greatest inventions in modern cardiac surgery. It is a life-saving device used to temporarily take over the work of the heart and lungs during open-heart surgeries. By circulating blood and providing oxygen artificially, it allows surgeons to operate on a still, blood-free heart.
What is a Heart-Lung Machine?
A heart-lung machine is a medical device used in open-heart surgery. It temporarily does the job of:
- Pumping blood (like the heart)
- Adding oxygen and removing carbon dioxide (like the lungs)
This process is called cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB).
In simple terms, it keeps the patient alive and stable while the surgeon works on the heart.
👉 Other names:
- Cardiopulmonary bypass machine
- Heart-lung bypass machine
- Artificial heart and lung machine
Table of Contents
Heart-Lung Machine Diagram
A typical heart-lung machine consists of:
- Venous line – carries deoxygenated blood from the body to the machine.
- Oxygenator – adds oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
- Pump – pushes oxygenated blood back to the body.
- Heat exchanger – controls patient’s body temperature.
- Arterial line – returns blood to the patient.
(Here you can insert a labeled diagram for blogs – “Heart-Lung Machine Diagram”)
Working Principle of Heart-Lung Machine
The working principle can be explained step by step:
- Blood Drainage – Blood from the patient’s body (via large veins) flows into the machine.
- Oxygenation – The machine supplies oxygen and removes carbon dioxide.
- Pumping – The oxygen-rich blood is pumped back to the body through arteries.
- Temperature Control – The machine can cool or warm the blood to protect organs.
This is how it bypasses the patient’s own heart and lungs.
👉 If you want technical details, you can find heart-lung machine working principle PDFs and cardiopulmonary bypass PPTs used in medical colleges.
Procedure: How is the Heart-Lung Machine Used in Surgery?
Here’s a simple explanation of what happens when the machine is used:
- Anesthesia – The patient is given general anesthesia.
- Cannulation – Tubes are inserted into large veins and arteries.
- Bypass Start – Blood starts flowing into the machine.
- Machine Takes Over – The machine does the pumping and oxygenation.
- Surgery on the Heart – The surgeon repairs valves, arteries, or congenital defects.
- Weaning Off – Slowly, the patient’s heart takes over again.
- Removal of Tubes – The patient’s blood circulation returns to normal.
This process can last from 30 minutes to several hours, depending on the surgery.
Types of Heart-Lung Machines
There are different designs and models of CPB machines, such as:
- Roller Pump Machines – Use rollers to push blood through tubing.
- Centrifugal Pump Machines – Use spinning rotors to move blood (safer, less damage to blood cells).
- Portable CPB Machines – Smaller, newer versions for specific cases.
- ECMO Machines – Advanced type used outside the operation theater (we’ll compare below).
When is a Heart-Lung Machine Needed?
The machine is commonly used in:
- Open-heart surgery
- Coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG)
- Heart valve repair or replacement
- Heart transplant surgery
- Repair of congenital heart defects
- Aortic aneurysm surgeries
Without this machine, many of these surgeries would not be possible.
Side Effects and Risks
Although lifesaving, it is not 100% risk-free. Possible side effects include:
- Blood clotting problems
- Stroke or brain injury (rare)
- Infection risk
- Kidney or lung complications
- Memory or concentration issues (called “pump head”)
- Low blood pressure
Doctors take strict precautions to minimize these risks.
Heart-Lung Machine vs ECMO
People often confuse heart-lung machine with ECMO (Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation). Here’s the difference:
| Feature | Heart-Lung Machine (CPB) | ECMO Machine |
|---|---|---|
| Use | During heart surgery | For long-term support in ICU |
| Duration | Few hours | Days to weeks |
| Mobility | Hospital operation theater | ICU, portable |
| Purpose | Stops heart for surgery | Supports heart/lungs until recovery or transplant |
| Complexity | More complex | Relatively simpler |
How Long Can a Person Be on a Heart-Lung Machine?
- Usually, only 3–6 hours during surgery.
- Longer use can damage blood cells and increase complications.
- For long-term support, doctors prefer ECMO instead of CPB.
Cost of Heart-Lung Machine
The price of a cardiopulmonary bypass machine depends on brand, model, and country:
- In India: ₹50 lakhs – ₹1.5 crore (approx. $60,000 – $180,000)
- Worldwide: $100,000 – $250,000
- Disposable tubing and oxygenators used per patient add extra cost.
For patients, the cost of heart surgery with bypass machine in India ranges from ₹2 lakhs – ₹7 lakhs, depending on hospital and surgery type.
Heart-Lung Machine PPT & PDF (For Students)
Many medical students and professionals look for:
- Cardiopulmonary Bypass PPT – for class presentations.
- Heart-Lung Machine Working Principle PDF – for detailed notes.
These resources explain:
- History of the machine
- Parts and functions
- Working steps
- Complications and prevention
You can easily find them online or request from medical institutions.
FAQs on Heart-Lung Machine
1. What is the difference between cardiopulmonary bypass and heart-lung machine?
Cardiopulmonary bypass is the process, while the heart-lung machine is the device that makes it possible.
2. What is a heart-lung bypass machine called?
It is also called the cardiopulmonary bypass machine (CPB).
3. What is the difference between a heart-lung machine and an ECMO?
- Heart-lung machine: Used during surgery, short-term.
- ECMO: Used in ICU, long-term life support.
4. What is the ECMO machine for cardiopulmonary bypass?
ECMO is a modified, portable version of bypass support but used outside surgery.
5. Can a person live without a heart-lung machine in surgery?
For many open-heart surgeries, survival without the machine is not possible.
Future of Heart-Lung Machines
- New machines are smaller, safer, and more efficient.
- Use of biocompatible materials reduces side effects.
- Artificial intelligence is being explored to improve monitoring.
- Portable machines may become more common in emergencies.
Conclusion
The heart-lung machine (cardiopulmonary bypass machine) is a true medical marvel. It allows surgeons to perform complex heart surgeries that save millions of lives every year.