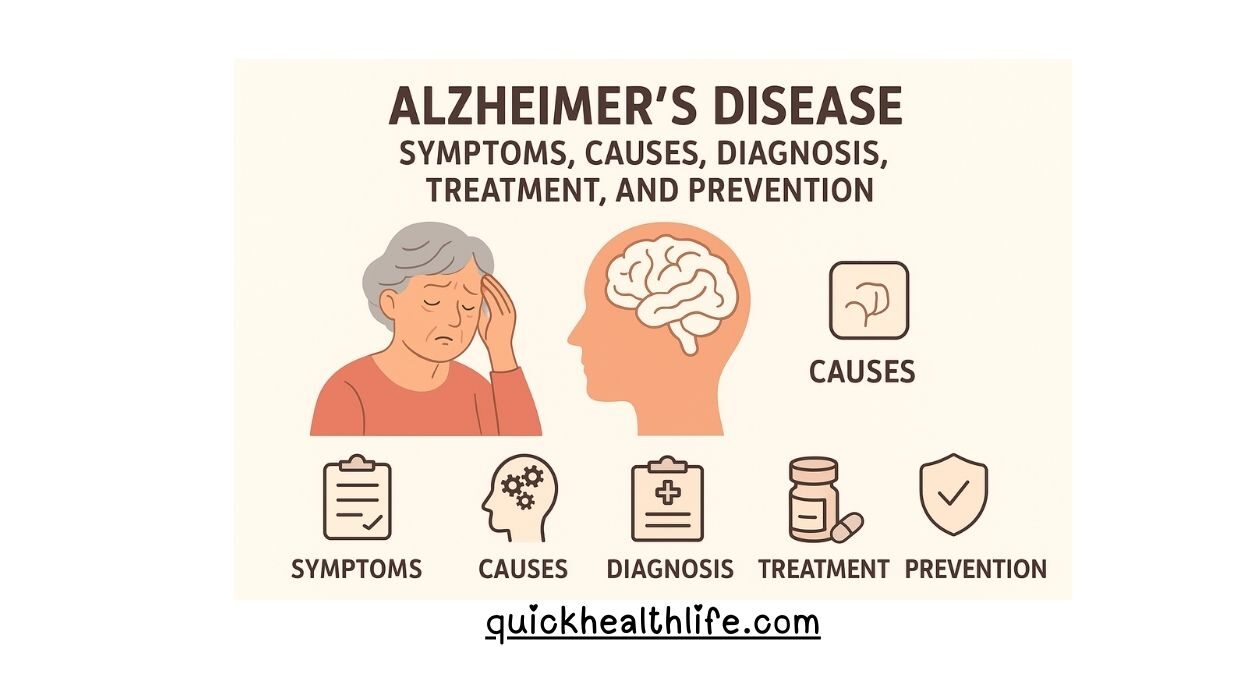
Alzheimer’s Disease is one of the most common health problems in the world today. It is a progressive brain disorder that slowly destroys memory, thinking skills, and the ability to carry out daily activities. Millions of families are struggling with this condition, making it a major public health challenge.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is a type of dementia that damages brain cells and interferes with memory, learning, and thinking abilities. It is the most common cause of dementia and usually affects people over the age of 65. However, younger people can also develop it, which is called early-onset Alzheimer’s.
It is not just normal memory loss due to aging—it is a serious medical condition that worsens with time if not managed properly.
Table of Contents
Alzheimer’s Disease Symptoms
Recognizing Alzheimer’s disease symptoms early is the key to better care.
Common Symptoms Include:
- Memory loss affecting daily life
- Confusion about time and place
- Difficulty completing routine tasks
- Misplacing things often
- Trouble with speech and writing
- Poor decision-making
- Personality and mood changes
What are the 7 signs of Alzheimer’s?
The 7 most common signs are:
- Memory loss disrupting daily life
- Trouble solving problems or planning
- Confusion about dates and places
- Difficulty performing familiar tasks
- Problems with language and communication
- Poor judgment and decision-making
- Social withdrawal and personality changes
If these symptoms appear, medical consultation should not be delayed.
Types of Alzheimer’s Disease
Understanding the types of Alzheimer’s disease helps in diagnosis and treatment.
Main Types:
- Early-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease – starts before age 65, often due to genetics.
- Late-Onset Alzheimer’s Disease – most common type, after age 65.
- Familial Alzheimer’s Disease – a rare inherited form.
What are the 5 types of Alzheimer’s disease?
Researchers also divide the condition into five stages:
- Preclinical Alzheimer’s (no visible symptoms yet)
- Mild cognitive impairment (MCI)
- Mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s
- Moderate dementia due to Alzheimer’s
- Severe dementia due to Alzheimer’s
Causes of Alzheimer’s Disease
What causes Alzheimer’s disease?
The exact cause is still not fully known, but a mix of genetic, lifestyle, and environmental factors plays a role.
The brain of an Alzheimer’s patient usually has:
- Beta-amyloid plaques: abnormal protein buildup between nerve cells.
- Tau tangles: twisted protein fibers inside brain cells.
- Loss of neurotransmitters: chemicals like acetylcholine are reduced.
Alzheimer’s disease caused by deficiency of
One major factor is Alzheimer’s disease caused by deficiency of acetylcholine, a brain chemical that helps with memory and learning. Deficiency of Vitamin B12 and folate may also worsen the condition.
What is the main cause of Alzheimer’s?
The main cause is the buildup of abnormal proteins in the brain that damage and kill nerve cells. Aging, family history, and unhealthy lifestyle choices increase the risk.
Risk Factors of Alzheimer’s Disease
Several factors can increase the risk of developing Alzheimer’s.
Common risk factors of Alzheimer’s disease:
- Age – chances rise after 65
- Genetics – family history increases risk
- Gender – women are at higher risk
- Head injuries – past trauma can contribute
- Lifestyle habits – smoking, alcohol, poor diet, and lack of exercise
- Medical conditions – diabetes, hypertension, and obesity
Diagnosis of Alzheimer’s Disease
Early and accurate diagnosis helps in better management.
Common methods include:
- Medical history check
- Neurological exams – reflexes, balance, and speech tests
- Cognitive tests – memory, attention, and problem-solving
- Brain imaging – MRI, CT, and PET scans
- Blood tests – to rule out vitamin deficiencies or thyroid issues
Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment
Currently, there is no cure, but Alzheimer’s disease treatment can slow down the progression and manage symptoms.
Alzheimer’s disease medication
- Cholinesterase inhibitors (Donepezil, Rivastigmine, Galantamine) – improve memory and thinking.
- Memantine – helps with moderate to severe Alzheimer’s by regulating glutamate.
- New therapies – ongoing research focuses on amyloid-targeting drugs.
Non-Medical Treatments
- Cognitive training (puzzles, memory games)
- Physical exercise (walking, yoga, meditation)
- Healthy diet (Mediterranean or DASH diet)
- Counseling and support groups for patients and caregivers
Prevention of Alzheimer’s Disease
How can you prevent Alzheimer’s?
While it cannot always be prevented, certain habits lower the risk:
- Eat a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids
- Engage in regular exercise to improve blood flow to the brain
- Stay mentally active with reading, puzzles, or learning new skills
- Maintain social connections to avoid isolation
- Control chronic conditions like diabetes, high blood pressure, and cholesterol
Living with Alzheimer’s
Living with Alzheimer’s is challenging, but proper care makes a big difference. Families need to create a safe home, maintain a routine, and provide emotional support. Caregivers should also take care of their own health while supporting the patient.
FAQs Of Alzheimer’s
1. What is the main cause of Alzheimer’s?
Abnormal protein buildup (amyloid and tau) in the brain is the main cause.
2. What are the 7 signs of Alzheimer’s?
Memory loss, confusion, problem-solving issues, language problems, disorientation, poor judgment, and social withdrawal.
3. What are the 5 types of Alzheimer’s disease?
Preclinical, mild cognitive impairment, mild dementia, moderate dementia, and severe dementia.
4. Alzheimer’s disease caused by deficiency of what?
It is linked to deficiency of acetylcholine, vitamin B12, and folate.
5. How can you prevent Alzheimer’s?
Healthy lifestyle choices like diet, exercise, mental activity, and controlling chronic conditions reduce risk.
6. What is Alzheimer’s disease medication used for?
It is used to manage symptoms and slow progression.
7. What causes Alzheimer’s disease?
Genetics, abnormal proteins, aging, and lifestyle factors.

[…] Read More: Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention […]
[…] Read More: Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention […]
[…] Read More: Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention […]
[…] Read More: Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis […]