Blood pressure fluctuates throughout the day due to activity, stress, diet, and even sleep. A single clinic measurement often fails to capture these variations, leading to misdiagnosis of conditions like hypertension. This is where a 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring device becomes invaluable. It records blood pressure at regular intervals over an entire day and night, providing a more accurate picture of cardiovascular health.
Table of Contents
What is an Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitor?
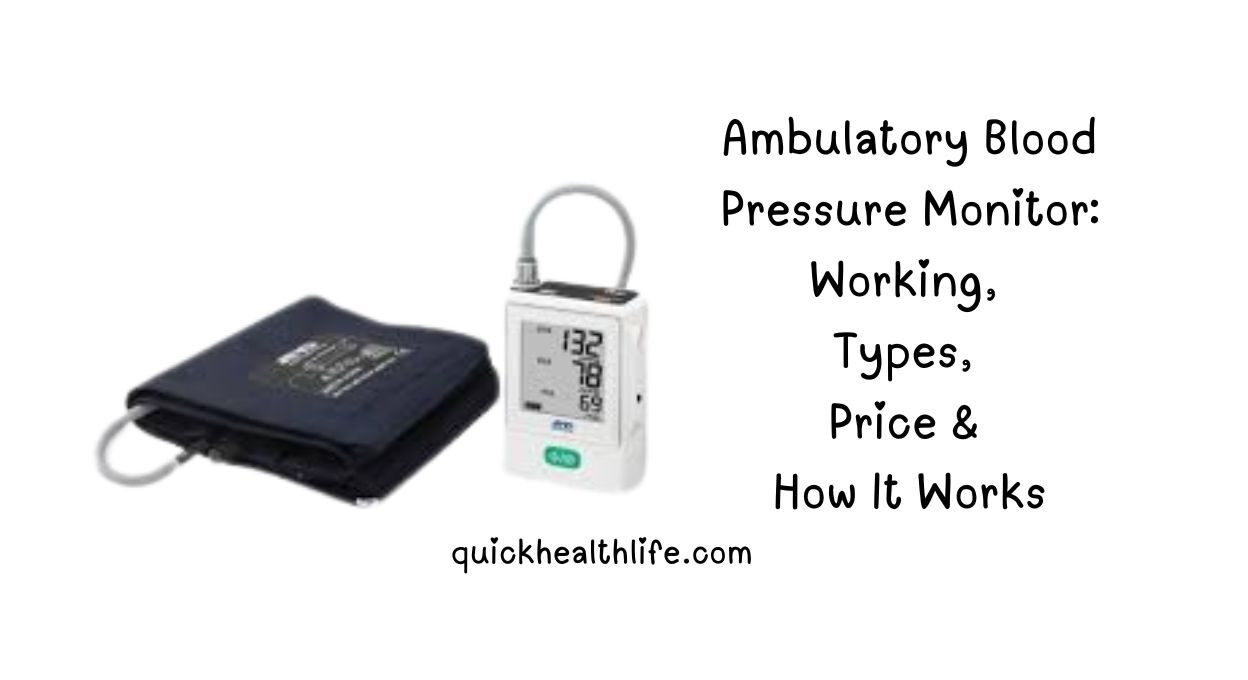
An ambulatory blood pressure monitor is a compact, portable device worn on the body to continuously record blood pressure. Unlike traditional cuffs used in clinics, it automatically inflates and deflates at set intervals, typically every 15–30 minutes during the day and 30–60 minutes at night.
The device includes three main components:
- A cuff worn around the upper arm
- A small monitor attached to a belt or strap
- Digital memory to store readings over 24 hours or longer
The collected data is then analyzed by healthcare professionals for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring interpretation.
Why Ambulatory Monitoring Matters
Conventional blood pressure readings can be misleading. For instance, some people show elevated pressure in clinical settings, known as “white-coat hypertension.” Others may have masked hypertension, where normal readings in the clinic disguise high levels at home.
Ambulatory monitoring helps to:
- Detect white-coat hypertension
- Identify masked hypertension
- Assess blood pressure variation throughout the day and night
- Evaluate treatment effectiveness in hypertensive patients
- Monitor nocturnal blood pressure patterns
These insights allow physicians to tailor treatments more effectively.
How Does a 24-Hour Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitor Work?
Wearing a 24 Hour Blood Pressure Monitor
The process begins with wearing a 24 hour blood pressure monitor on the non-dominant arm. The cuff automatically inflates and deflates at scheduled times, recording each measurement. Patients are advised to go about daily routines but avoid excessive movement during readings.
How to Sleep with a 24-Hour Blood Pressure Monitor
Many patients wonder how to sleep with a 24-hour blood pressure monitor. While it may feel uncomfortable initially, adjusting sleeping positions helps. Sleeping on the opposite side of the cuff and ensuring loose clothing reduces disturbances. Nighttime readings are essential, as blood pressure typically dips during sleep.
Daily Activities
The device allows patients to work, walk, and eat as usual. However, it is not waterproof, which raises the common question: can I take off my 24 hour blood pressure monitor to shower? The answer is no—removing it interrupts the data. Instead, patients are advised to use sponge baths until monitoring is complete.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Guidelines
Medical professionals follow specific ambulatory blood pressure monitoring guidelines to ensure accurate results:
- Duration: Typically 24 hours, though some cases may require 48 hours.
- Frequency of Readings: Every 15–30 minutes during daytime and every 30–60 minutes at night.
- Interpretation Standards:
- Normal daytime average: < 135/85 mmHg
- Normal nighttime average: < 120/70 mmHg
- Normal 24-hour average: < 130/80 mmHg
Deviation from these values indicates hypertension or abnormal blood pressure patterns.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Interpretation
Interpreting results involves analyzing average values, daytime versus nighttime readings, and circadian patterns. Physicians look for:
- Dipping Status: A healthy individual shows a 10–20% reduction in nighttime pressure. Lack of dipping or reverse dipping suggests increased cardiovascular risk.
- Morning Surge: Excessive morning rise indicates higher chances of stroke or heart attack.
- Blood Pressure Variability: Unusual fluctuations highlight underlying health concerns.
This ambulatory blood pressure monitoring interpretation provides critical insight that a single clinic reading cannot capture.
Types of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitors
- Standard 24-Hour Monitors – Used for routine hypertension evaluation.
- Extended Monitoring Devices – Record data for up to 48–72 hours.
- Wireless Monitors – Sync with smartphones and allow remote physician access.
- Specialized Pediatric Monitors – Designed for children with smaller cuff sizes.
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring Price
The ambulatory blood pressure monitoring price varies depending on the device type and location.
- Rental or Clinic-Based Monitoring: ₹1,500–₹4,000 (India) or $50–$150 (USA) per session.
- Home Purchase Devices: ₹10,000–₹25,000 (India) or $200–$500 (USA).
- Advanced Wireless Models: Higher-end devices can exceed ₹40,000 or $700.
Prices differ based on technology, accuracy, and whether a healthcare professional supervises the monitoring.
Where to Find Ambulatory Monitoring Services
Patients often search for ambulatory blood pressure monitoring near me when prescribed this test. Services are widely available in:
- Cardiology clinics
- Multispecialty hospitals
- Diagnostic laboratories
- Online health platforms offering home-based monitoring
Accessibility is improving, making it easier for patients to get accurate diagnoses.
Advantages of Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring
- Provides multiple readings in real-life settings
- Detects hidden forms of hypertension
- Monitors medication effectiveness
- Identifies high-risk nocturnal blood pressure patterns
- Reduces misdiagnosis compared to clinic readings
Limitations and Challenges
- Discomfort during sleep due to frequent cuff inflation
- Inconvenience in bathing as the device cannot be removed
- Slightly higher cost compared to standard monitoring
- Possible skin irritation from prolonged cuff use
Despite these challenges, the benefits outweigh temporary inconveniences.
Tips for Patients Undergoing Ambulatory Monitoring
- Wear loose-fitting clothes for comfort
- Keep the monitor dry at all times
- Stay still when the cuff inflates for accurate readings
- Avoid vigorous physical activity during monitoring
- Maintain a diary of daily activities and symptoms to assist physicians in interpretation
Future of Blood Pressure Monitoring
With technological advancements, new devices are becoming smaller, more comfortable, and more accurate. Innovations like cuffless sensors, wearable patches, and AI-driven interpretation will redefine how blood pressure is monitored. Soon, real-time cloud-based reporting may allow continuous physician supervision.
Conclusion
Ambulatory blood pressure monitoring is a revolutionary approach to understanding blood pressure fluctuations. By using a 24-hour ambulatory blood pressure monitoring device, doctors gain detailed insights into real-life blood pressure variations. While patients may feel slight discomfort when wearing a 24 hour blood pressure monitor, following proper ambulatory blood pressure monitoring guidelines ensures reliable results.