What is Anal Cancer?
Anal cancer is a type of cancer that develops in the anus, which is the opening at the end of the digestive tract where stool leaves the body.
It happens when the cells in the lining of the anus grow abnormally and start forming a tumor. Unlike hemorrhoids (piles), which are swollen veins, anal cancer involves abnormal cell growth that can spread to other parts of the body if not treated in time.
Though anal cancer is not as common as other cancers like colon or lung cancer, it is still serious and needs medical attention.
Table of Contents
What Causes Anal Cancer?
Understanding the causes of anal cancer is important because it helps us know the risk factors.
The main causes and risks include:
1. HPV Infection
The most common cause is human papillomavirus (HPV). It is a very common sexually transmitted infection. Certain types of HPV can cause cancer in the anus, cervix, and throat.
2. Weakened Immune System
People with weak immunity – for example, HIV-positive patients or those on long-term immune-suppressing medicines – are at higher risk.
3. Age Factor
Most cases are seen in people above 50 years of age.
4. Smoking
Smoking damages cells and makes them more likely to turn into cancer.
5. History of Anal Warts
Anal warts (caused by HPV) increase the risk of anal cancer later in life.
6. Multiple Sexual Partners
More partners increase the risk of HPV infection, which is the leading cause.
Read More: Alkaptonuria Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment & FAQ
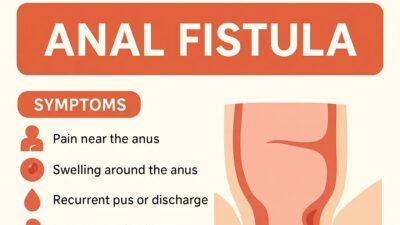
What Are the Symptoms of Anal Cancer?
The early signs of anal cancer can be confusing because they are very similar to common problems like piles or fissures. That’s why many people ignore them at first.
Here are the common anal cancer symptoms:
- Lump near the anus – a small growth or swelling that doesn’t go away.
- Pain or discomfort in or around the anus.
- Bleeding from the anus (may be mistaken for hemorrhoids).
- Itching or irritation around the anal area.
- Change in bowel habits – constipation, narrow stool, or frequent urge to pass stool.
- Discharge from the anus.
- Swollen lymph nodes in the groin.
If you notice any of these symptoms for more than 2 weeks, you should see a doctor.
Hemorrhoids vs. Anal Cancer:
This is one of the most common questions people ask: “How do I know if I have hemorrhoids or cancer?”
Here’s the difference:
- Hemorrhoids are swollen veins. They usually cause pain, itching, and bleeding but do not form a hard lump that grows.
- Anal cancer often causes a hard lump, persistent pain, bleeding, and discharge, and symptoms keep getting worse over time.
👉 If symptoms don’t improve with normal treatment for piles, consult a doctor immediately for tests.
Read More: Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment, and Prevention
Tests and Diagnosis of Anal Cancer
If your doctor suspects anal cancer, they may suggest the following tests:
1. Physical Examination
The doctor checks the anal area and feels for lumps.
2. Digital Rectal Exam (DRE)
The doctor inserts a finger (with gloves) inside the rectum to feel for any growth.
3. Anoscopy
A small tube with a light is inserted to see inside the anus.
4. Biopsy
If a suspicious lump is found, a small piece of tissue is taken and tested under a microscope to confirm cancer.
5. Imaging Tests
CT scan, MRI, or PET scan may be done to check if the cancer has spread.
Stages of Anal Cancer
Like all cancers, anal cancer is divided into stages depending on how far it has spread:
- Stage 0: Abnormal cells are present but not yet cancer.
- Stage I: Small tumor (less than 2 cm), only in the anus.
- Stage II: Tumor larger than 2 cm but not spread outside.
- Stage III: Cancer has spread to nearby lymph nodes or organs.
- Stage IV: Cancer has spread to distant organs (metastasis).
Treatment for Anal Cancer
Treatment depends on the stage of cancer, overall health, and age. The main treatments are:
1. Chemoradiation (Chemo + Radiation)
This is the most common treatment.
- Radiation therapy uses high-energy rays to kill cancer cells.
- Chemotherapy uses medicines to make radiation more effective.
Together, they work well for most patients.
2. Surgery
If cancer doesn’t respond to chemoradiation, surgery may be needed to remove the tumor. In some advanced cases, part of the rectum may also be removed.
3. Targeted Therapy
Some new medicines directly target cancer cells without harming normal cells.
4. Immunotherapy
For patients with advanced cancer, drugs that boost the immune system may be used.
Read More: Alcohol Misuse: Risks, Treatment, Symptoms, Types, Causes
Anal Cancer Survival Rate
Now the most important question: “Can you die from anal cancer?”
The answer is – yes, if it is not treated on time. But the good news is that anal cancer is curable in many cases, especially when detected early.
According to research:
- The 5-year survival rate for localized anal cancer (not spread) is around 80–85%.
- If cancer has spread to nearby areas, the survival rate is around 60%.
- If it has spread to distant organs, survival drops to 30–35%.
So early detection is the key to cure.
Is Anal Cancer Curable?
Yes, in many cases, anal cancer is curable – especially when diagnosed in stage I or II. Modern treatment with chemoradiation is very effective.
That’s why don’t ignore symptoms like bleeding or lumps in the anus. Early checkup can save lives.
Living with Anal Cancer: Next Steps
If you or a loved one is diagnosed with anal cancer:
- Don’t panic – it is treatable.
- Follow the treatment plan given by your doctor.
- Eat a healthy diet with fruits, vegetables, and whole grains.
- Stay active – light exercise improves mood and immunity.
- Quit smoking and alcohol.
- Go for regular checkups to monitor progress.
Prevention of Anal Cancer
You can reduce the risk by following these steps:
- HPV vaccination – protects against the main virus causing anal cancer.
- Safe sex practices – use protection to reduce HPV infection risk.
- Quit smoking.
- Boost immunity by eating healthy and exercising.
- Regular health checkups, especially if you are above 50.
Read More: Adenomyosis Disease: Overview, Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis & Treatment
FAQs About Anal Cancer
1. Can you die from anal cancer?
Yes, if not treated in time. But with early treatment, most patients live a normal life.
2. Is anal cancer curable?
Yes, especially if detected early.
3. What are the signs of anal cancer?
Lump in the anus, bleeding, pain, itching, and changes in bowel habits.
4. What causes anal cancer?
The main cause is HPV infection, along with risk factors like smoking and weak immunity.
5. How do I know if I have hemorrhoids or cancer?
Hemorrhoids usually cause pain and itching but not a hard growing lump. If symptoms persist, see a doctor for tests.
6. What is the anal cancer survival rate?
Around 80% for early stage, lower if cancer spreads.