What is Angelman Syndrome?
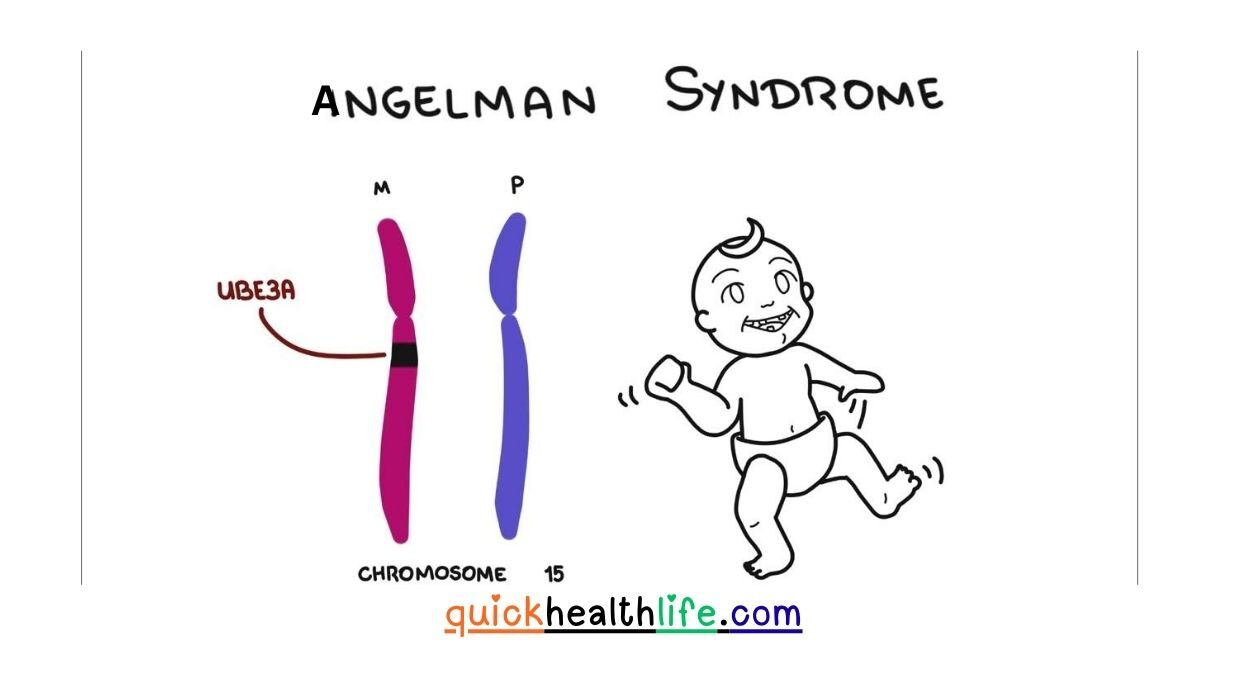
Angelman Syndrome is a rare genetic disorder that mainly affects the nervous system. It leads to developmental delays, problems with speech, balance issues, and sometimes seizures.
Children with Angelman Syndrome often have a happy and excitable personality. They smile and laugh frequently, which is why the condition was earlier known as the “Happy Puppet Syndrome.”
Table of Contents
Symptoms and Causes
Common Symptoms of Angelman Syndrome
- Developmental delay – delayed sitting, crawling, walking, or talking
- Speech problems – very little or no speech ability
- Frequent smiling and laughter
- Hyperactivity and short attention span
- Sleep disturbances – difficulty falling asleep or staying asleep
- Seizures (epilepsy) – usually start in childhood
- Movement and balance issues – unsteady walking, jerky movements
- Intellectual disability – mild to severe learning difficulties
Facial and Physical Features
Some children may also have:
- Wide mouth with frequent smiles
- Protruding tongue
- Fair skin and light-colored hair (in some cases)
- Small head size (microcephaly)
What Causes Angelman Syndrome?
The main cause of Angelman Syndrome is a problem in the UBE3A gene located on chromosome 15. This gene is important for brain development and functioning.
The condition usually happens because:
- The UBE3A gene from the mother is missing or damaged.
- The father’s copy of the gene is present but inactive in the brain.
This genetic error affects how the brain works, leading to the typical symptoms of Angelman Syndrome.
Read More: Alkaptonuria Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis, Treatment & FAQ
Angelman Syndrome Inheritance and Genetics
Angelman Syndrome is usually not inherited in a traditional way. In most cases, it happens spontaneously (without family history).
However, in rare cases:
- It can be passed from parents to children through genetic mutations.
- If a family already has one child with Angelman Syndrome, there is a slightly higher chance for future children to be affected.
Genetic counseling is highly recommended for families planning children if Angelman Syndrome is present in the family history.
Angelman Syndrome vs Autism vs Prader-Willi Syndrome
Many people confuse Angelman Syndrome with Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) or Prader-Willi Syndrome (PWS). Let’s compare them in a simple table.
| Feature | Angelman Syndrome | Autism | Prader-Willi Syndrome |
|---|---|---|---|
| Speech | Very limited or no speech | May have speech delay | Speech usually present but can be delayed |
| Behavior | Happy, frequent laughter | Social communication difficulties | Food-seeking behavior, overeating |
| Movement | Unsteady, jerky movements | May have motor delays | Poor muscle tone, obesity |
| Seizures | Common | Less common | Rare |
| Genetics | UBE3A gene (maternal chromosome 15) | Complex, multiple genes | Paternal chromosome 15 deletion |
Read More: Alzheimer’s Disease: Symptoms, Causes, Diagnosis
Angelman Syndrome Diagnosis Tests
Diagnosing Angelman Syndrome can be challenging because symptoms appear slowly over time. Doctors may use:
- Clinical Examination – observing developmental delays, movement issues, and behavior.
- Genetic Testing – blood tests to check for changes in chromosome 15 and the UBE3A gene.
- EEG (Electroencephalogram) – to check brain wave patterns, especially if seizures are present.
- MRI or CT Scan – sometimes used to rule out other brain-related conditions.
Early diagnosis is important so that therapy and treatment can start as soon as possible.
Angelman Syndrome Treatment Options
Currently, there is no permanent cure for Angelman Syndrome. But treatments focus on improving the child’s quality of life.
Common Treatment Methods:
- Physical therapy – to improve movement and coordination
- Speech therapy – to help with communication (using sign language or communication devices)
- Occupational therapy – to improve daily activities and independence
- Seizure management – medications to control epilepsy
- Sleep management – medicines and sleep routines to reduce sleep disturbances
- Behavioral therapy – to manage hyperactivity and improve focus
Doctors usually create a personalized treatment plan based on the child’s needs.
Angelman Syndrome Prevention
Unfortunately, there is no way to prevent Angelman Syndrome completely, because it is caused by genetic changes.
But couples with a family history of the condition can consider:
- Genetic counseling before pregnancy
- Prenatal testing (in some cases) to check for risks
Awareness and early intervention remain the best way to manage the condition.
Read More: Alcohol Misuse: Risks, Treatment, Symptoms, Types, Causes
Angelman Syndrome Life Expectancy
The good news is that people with Angelman Syndrome usually have a normal life expectancy. With proper care, they can live long and fulfilling lives.
However, challenges like seizures, sleep problems, and movement issues may require lifelong support. Most individuals need help in daily activities throughout life, but with therapy and family support, they can be happy and active.
Angelman Syndrome Research and Gene Therapy
In recent years, research on Angelman Syndrome has advanced rapidly. Scientists are exploring:
- Gene therapy – to reactivate the father’s silent UBE3A gene in the brain
- New seizure medicines – to control epilepsy better
- Improved therapies – focusing on communication and independence
Although these treatments are still in the research stage, they bring hope for future generations.
ICD-10 Code for Angelman Syndrome
For medical and insurance purposes, Angelman Syndrome is classified under the ICD-10 code: Q93.51.
This code is used by doctors, hospitals, and researchers worldwide.
Final Thoughts by Umesh Yadav
As a health blogger with 3 years of writing experience, I know how confusing medical terms can be. That’s why I always try to simplify them for you.
Angelman Syndrome is a rare but manageable condition. While it cannot be cured completely, early diagnosis, therapies, and family support can make a big difference in the child’s life.