What is Angina?
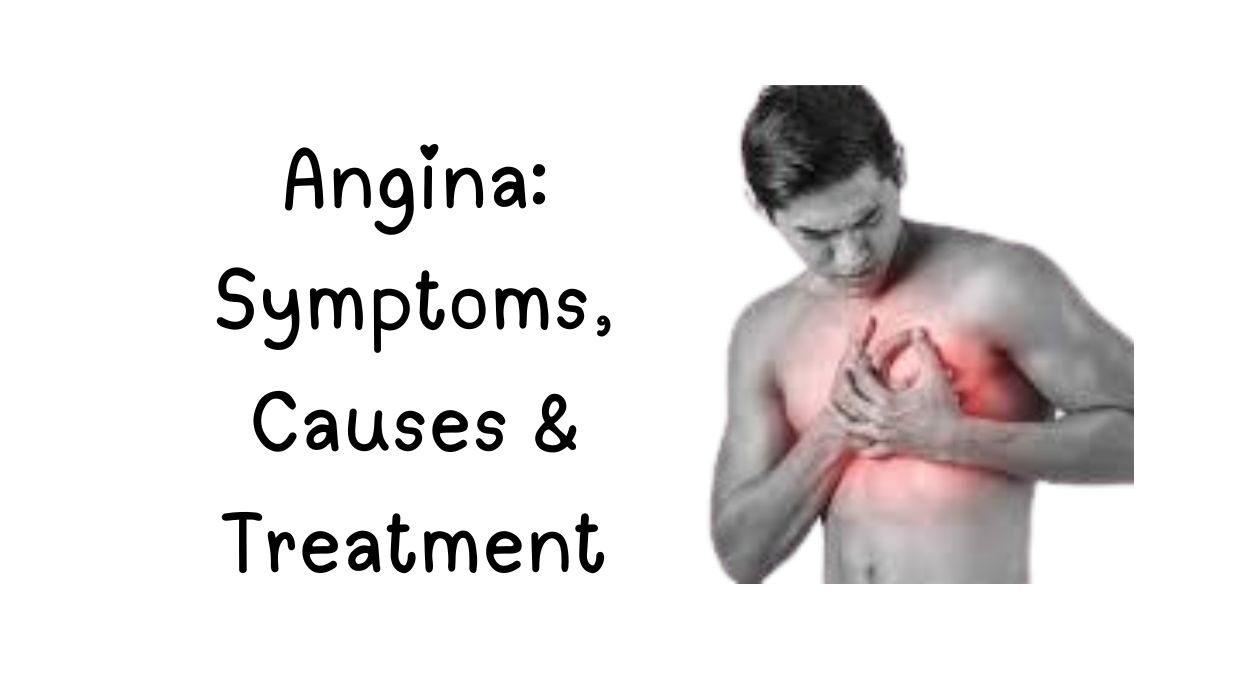
Angina, also known as angina pectoris, is chest pain or discomfort that occurs when part of your heart muscle does not get enough oxygen-rich blood. Angina pain can feel like pressure, squeezing, tightness, or burning in your chest. The discomfort can also spread to your shoulders, arms, neck, jaw, or back, just like a heart attack.
What does angina feel like?
Most people with angina describe having chest pressure or pain. It can be mild or more severe. It’s common to feel vague discomfort, rather than actual pain. Angina might feel like:
- Squeezing
- Tightness
- Heaviness
- Crushing
- Burning, like heartburn or indigestion
This discomfort may spread to your jaw, teeth, shoulders, arm or back.
Angina can happen alongside other symptoms, like:
- Sweating
- Dizziness
- Weakness
- Gas or bloating
- Upset stomach or nausea
- Feeling clammy
- Skin that’s paler than usual
- Feeling of impending doom
Table of Contents
Angina in women
Symptoms of angina in women can be different from the classic angina symptoms. These differences may lead to delays in seeking treatment. For example, chest pain may not be the only symptom or the most common symptom. Other symptoms of angina in women may include:
- Discomfort in the neck, jaw, teeth or back.
- Nausea.
- Shortness of breath.
- Stabbing pain instead of chest pressure.
- Stomach pain.
Types of Angina
Angina is chest pain or discomfort caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. There are four main types, each with distinct characteristics:
1. Stable Angina
- Trigger: Physical exertion or stress
- Duration: 5-15 minutes
- Relief: Rest or nitroglycerin
- Pattern: Predictable symptoms
- Risk: Warning sign of potential heart attack
2. Unstable Angina
- Trigger: Occurs at rest
- Duration: Longer than 20 minutes
- Relief: Doesn’t resolve with rest/medication
- Pattern: New, worsening, or unpredictable
- Risk: Often precedes heart attack
3. Variant (Prinzmetal’s) Angina
- Trigger: Coronary artery spasm (often at rest)
- Duration: 5-30 minutes (typically midnight-early morning)
- Relief: Calcium channel blockers
- Pattern: Cyclic, often same time daily
- Risk: Can cause dangerous arrhythmias
4. Microvascular Angina
- Trigger: Daily activities
- Duration: 10-30 minutes
- Relief: May not respond to nitroglycerin
- Pattern: More frequent in women
- Risk: Indicates small vessel disease
What is the main cause of angina?
What causes angina?
Reduced blood flow to your heart causes angina. Your heart may not get enough blood due to:
- Coronary artery disease (CAD): This is the most common cause of angina. It happens when plaque builds up in your coronary arteries.
- Coronary microvascular disease: This means tiny arteries in your heart are damaged.
- Coronary artery spasm: Your coronary arteries quickly tighten and then open up. You can have this condition without having coronary artery disease.
Angina Treatment
1. Medications for Angina Relief
| Medication Type | How It Works | Examples | Usage |
|---|---|---|---|
| Nitrates | Dilates blood vessels | Nitroglycerin | Acute attacks |
| Beta-blockers | Reduces heart workload | Metoprolol, Atenolol | Daily prevention |
| Calcium channel blockers | Relaxes arteries | Amlodipine, Diltiazem | Variant angina |
| Statins | Lowers cholesterol | Atorvastatin, Rosuvastatin | Long-term management |
| Antiplatelets | Prevents clots | Aspirin, Clopidogrel | Risk reduction |
2. Medical Procedures
- Angioplasty & Stenting: Opens blocked arteries (90% success rate)
- CABG Surgery: Bypass for multiple blockages
- Enhanced External Counterpulsation (EECP): Non-invasive option for refractory angina
3. Essential Lifestyle Changes
✔ Heart-healthy diet: Mediterranean or DASH diet
✔ Regular exercise: 150 mins/week moderate activity
✔ Smoking cessation: Doubles improvement in symptoms
✔ Stress management: Yoga, meditation proven effective
Angina Prevention
Risk Factor Management
| Risk Factor | Target | How to Achieve |
|---|---|---|
| Blood Pressure | <130/80 mmHg | Limit salt, take medications |
| Cholesterol | LDL <70 mg/dL | Statins, healthy fats |
| Blood Sugar | HbA1c <7% | Low-glycemic diet |
| Weight | BMI 18.5-25 | Portion control, activity |
When to Seek Emergency Care
Chest pain >15 minutes
Pain with:
- Cold sweats
- Nausea/vomiting
- Radiating to arm/jaw
First-ever angina episode
Angina Procedures
1. Percutaneous Coronary Intervention (PCI)
- What: Balloon angioplasty + stent placement
- Success Rate: 90% for single vessel disease
- Recovery: 1-2 days hospitalization
2. Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
- What: Vein/artery graft around blockages
- Best For: Multiple blockages
- Recovery: 4-6 weeks
Procedure Comparison
| Factor | PCI | CABG |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Minimal | Major surgery |
| Hospital Stay | 1-2 days | 5-7 days |
| Longevity | 5-10 years | 10-15 years |
| Best For | 1-2 blockages | Multiple blockages |