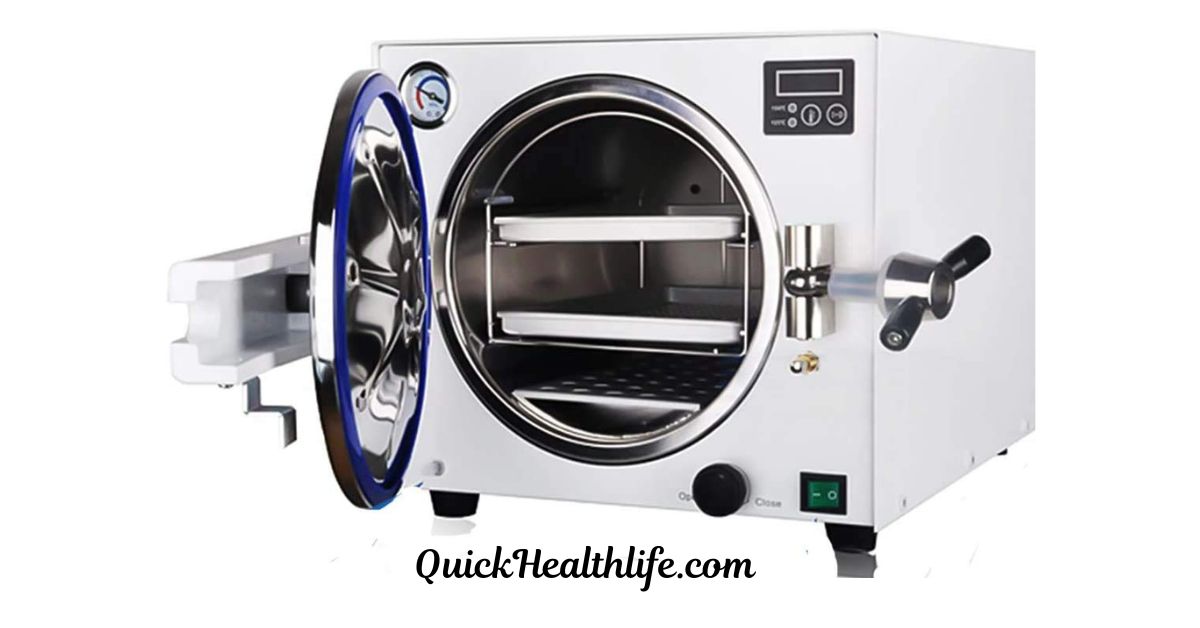
In hospitals, laboratories, and clinics, infection control is a top priority. One essential device used for sterilization is the autoclave machine. This machine ensures that medical instruments, glassware, and surgical tools are free from harmful bacteria, viruses, and spores.
What is an Autoclave Machine?
An autoclave machine is a device that uses steam under pressure to kill microorganisms on medical instruments and other materials. It’s a reliable and effective sterilization method widely used in:
- Hospitals
- Dental clinics
- Research laboratories
- Pharmaceutical industries
- Tattoo studios and beauty clinics
Autoclaving ensures that even the most resistant bacteria and spores are destroyed, providing a completely sterile environment for reuse.
Table of Contents
What Does an Autoclave Machine Do?
The main function of an autoclave machine is sterilization. It eliminates all forms of microbial life — including spores, fungi, and viruses — by applying moist heat (steam) at high temperature and pressure for a fixed time.
Principle of Autoclave Machine
The autoclave works on the principle of moist heat sterilization using steam under pressure. This is based on Charles’ and Boyle’s laws — when pressure increases, the boiling point of water rises, producing hotter steam that can destroy microorganisms faster.
In simple terms:
- Steam at 121 °C and pressure of 15 psi can kill most bacteria and spores within 15–20 minutes.
- The heat denatures the proteins of microorganisms, leading to complete sterilization.
Main Parts of an Autoclave Machine
Below are the key components that make the autoclave work efficiently:
| Part Name | Function |
|---|---|
| Chamber | The main area where instruments are placed for sterilization. |
| Pressure Gauge | Displays internal pressure during operation. |
| Temperature Controller | Regulates the internal temperature. |
| Safety Valve | Prevents excessive pressure buildup. |
| Steam Generator / Boiler | Produces steam for sterilization. |
| Drain Valve | Removes condensed water after each cycle. |
| Door/Locking Mechanism | Ensures the chamber is sealed tightly during operation. |
| Indicator Lights | Show whether the cycle is running or complete. |
Autoclave Machine Temperature and Pressure
The effectiveness of an autoclave depends on the right temperature, pressure, and time combination.
| Temperature (°C) | Pressure (psi) | Time Required | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| 121 °C | 15 psi | 15–20 minutes | Standard sterilization (instruments, dressings) |
| 126 °C | 20 psi | 10–15 minutes | Rapid sterilization |
| 134 °C | 30 psi | 3–5 minutes | Flash sterilization for emergency tools |
Why 15 minutes at 121 °C?
Because this combination ensures the destruction of even the toughest bacterial spores like Geobacillus stearothermophilus.
Uses of Autoclave Machine
Autoclaves play a vital role in healthcare and scientific fields. Let’s explore the main uses:
- Hospital Sterilization
- Surgical tools, dressings, and glassware.
- Dental Clinics
- Sterilizing dental mirrors, forceps, and handpieces.
- Laboratories
- Cleaning glass beakers, test tubes, and culture media.
- Pharmaceutical Industry
- Sterilizing culture media, solutions, and packaging.
- Tattoo & Beauty Clinics
- Sterilizing needles, scissors, and reusable tools.
- Research Institutions
- Ensuring aseptic conditions during experiments.
How Does an Autoclave Machine Work?
The working process of an autoclave can be divided into four simple stages:
- Loading Stage
- Instruments are cleaned and placed properly inside the chamber.
- Air gaps should be avoided for proper steam circulation.
- Heating and Pressurization
- Steam is generated and injected into the chamber.
- Temperature rises to 121 °C or higher at specific pressure.
- Sterilization Hold Time
- The set temperature and pressure are maintained for 15–20 minutes.
- Microorganisms and spores are completely destroyed.
- Depressurization and Drying
- Steam is released safely through the exhaust valve.
- Instruments dry and cool before removal.
Types of Autoclave Machines
There are several types of autoclaves depending on their use and design.
1. Gravity Displacement Autoclave
- The most common type in hospitals.
- Steam enters from the top and pushes out air from the bottom.
- Ideal for liquids and solid instruments.
2. Pre-Vacuum (High-Vacuum) Autoclave
- Uses a vacuum pump to remove air before steam enters.
- Provides faster and more efficient sterilization.
- Suitable for surgical packs and wrapped items.
3. Steam Flush Pressure Pulse (SFPP) Autoclave
- Replaces vacuum pumps with pressure pulses.
- Reduces cycle time and increases steam penetration.
4. Portable Autoclave
- Small-sized, ideal for clinics and field work.
- Works with electricity or gas.
5. Vertical Autoclave
- Cylindrical, space-saving model used in laboratories.
- Easy to operate and maintain.
6. Horizontal Autoclave
- Large capacity, used in hospitals and industries.
- Suitable for bulk sterilization.
Autoclave Machine Price in India (2025)
Prices vary according to size, type, and brand.
| Autoclave Type | Capacity | Approx. Price (INR) |
|---|---|---|
| Portable Autoclave | 10–20 L | ₹6,000 – ₹15,000 |
| Vertical Autoclave | 35–75 L | ₹20,000 – ₹60,000 |
| Horizontal Autoclave | 100–500 L | ₹80,000 – ₹3 Lakh |
| High-Vacuum Autoclave | 100 L+ | ₹2 Lakh – ₹6 Lakh |
| Industrial Autoclave | Custom | ₹5 Lakh – ₹20 Lakh+ |
Tip: Always buy from certified medical equipment suppliers and ensure the machine follows ISO 13485 and CE standards.
Advantages of Using an Autoclave Machine
- 100% effective sterilization
- Eco-friendly (uses only water and electricity)
- No toxic chemicals required
- Safe and reliable for daily hospital use
- Cost-effective for long-term use
Limitations of Autoclave Machine
- Not suitable for heat-sensitive materials (plastics, rubber).
- Requires regular maintenance and calibration.
- Improper loading can reduce sterilization efficiency.
- Moisture can damage some instruments if not dried properly.
Which Bacteria Is Not Killed by Autoclave?
Most bacteria, including spores, are killed by autoclaving. However, prions (infectious proteins that cause diseases like Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease) may resist normal autoclaving conditions and require extended cycles at higher temperatures.
What Is Autoclaving for 15 Minutes?
“Autoclaving for 15 minutes at 121 °C under 15 psi” is the standard sterilization cycle used in most hospitals and labs.
It ensures complete elimination of bacteria and spores without damaging the instruments.
Autoclave Machine for Hospitals
In hospitals, autoclaves are used daily for sterilizing surgical tools, linens, and glassware.
Modern hospital autoclaves come with automatic cycles, digital displays, and safety interlocks, making the process fast and reliable.
Maintenance & Safety Tips
- Always check water levels before operation.
- Do not overload the chamber.
- Clean the drain and gasket regularly.
- Calibrate temperature and pressure gauges periodically.
- Wear protective gloves when removing hot instruments.
FAQs About Autoclavee Machine
1. What is the main use of an autoclave machine?
To sterilize medical and laboratory instruments using steam under pressure.
2. What is the working temperature of an autoclave?
Usually between 121 °C and 134 °C, depending on the type of material.
3. What is the function of an autoclave?
To kill microorganisms and spores, ensuring instruments are safe for reuse.
4. Which bacteria is not killed by autoclave?
Prions are highly resistant; extended sterilization is required.
5. What does 15 minutes mean in autoclaving?
It’s the standard cycle time for effective sterilization at 121 °C and 15 psi.
6. What are the main parts of an autoclave machine?
Chamber, boiler, pressure gauge, safety valve, and door lock.
7. Can I use an autoclave at home?
Portable versions exist, but they should be operated carefully following safety guidelines.
8. How do I know if sterilization is successful?
Use biological or chemical indicators to verify sterilization effectiveness.