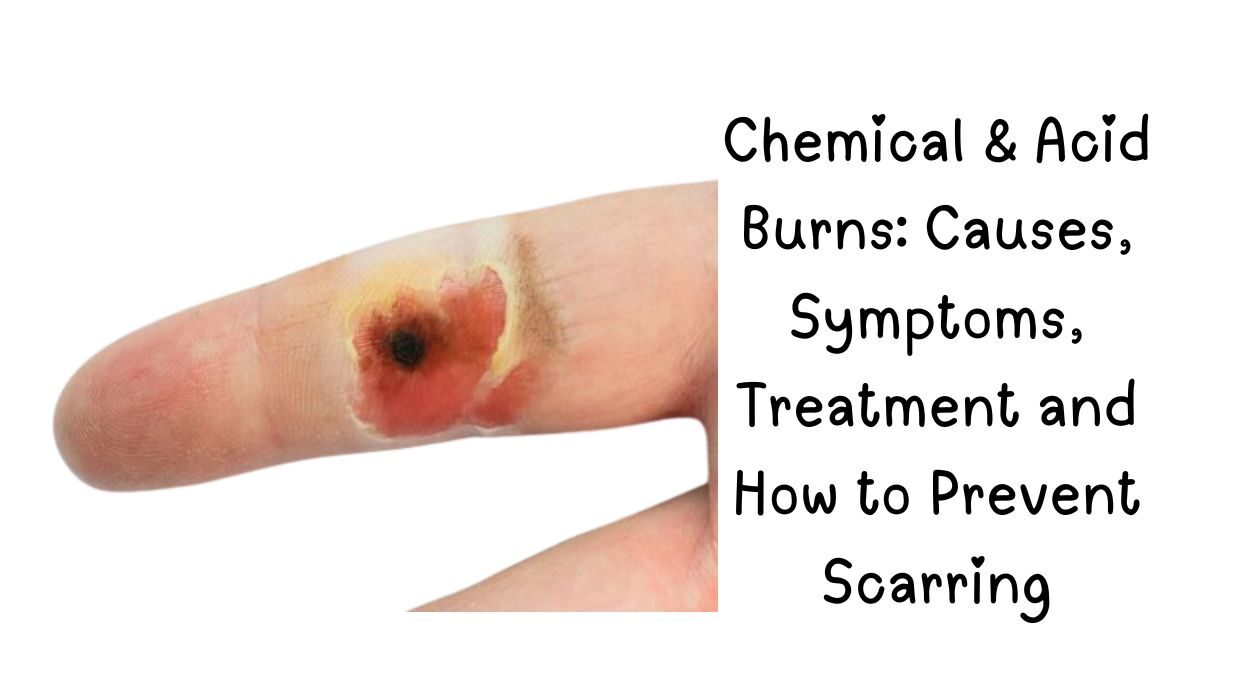
Chemical and acid burns can cause severe skin damage if not treated properly. Whether from household cleaners, industrial chemicals, or cosmetic products, knowing how to respond can prevent long-term harm.
What Are Chemical Burns And Acid Burns ?
Chemical burns occur when the skin or eyes come into contact with irritants like acids, alkalis, or solvents. These substances can cause tissue damage that ranges from minor irritation to deep wounds.
Acid burns typically cause coagulation necrosis, forming a hard scab-like layer. On the other hand, alkali burns are more severe, penetrating deeper into tissue.
Table of Contents
Types of Chemical Burns
| Type of Burn | Description | Common Causes |
|---|---|---|
| Acid Burns | Dry, leathery wound (coagulation necrosis) | Battery acid, hydrochloric acid |
| Alkali Burns | Deep, penetrating damage (liquefaction necrosis) | Drain cleaner, ammonia |
| Irritant Burns | Redness, peeling, mild damage | Bleach, detergents |
| Oxidizing Burns | Heat release worsens injury | Hydrogen peroxide, pool chemicals |
Common Household & Industrial Chemicals That Burn
Household Products
- Bleach (sodium hypochlorite)
- Drain cleaners (lye, sulfuric acid)
- Nail polish remover (acetone)
- Battery acid (sulfuric acid)
- Oven cleaners (sodium hydroxide)
Industrial & Medical Chemicals
- Hydrochloric acid (cleaning agents)
- Ammonia (fertilizers, refrigerants)
- Phenol (disinfectants)
- Chemical peels (salicylic acid, TCA)
Chemical Burn Symptoms
Chemical burns range from mild irritation to life-threatening injuries. Here’s how to assess severity:
Mild Chemical Burns (First-Degree)
- Redness (like a sunburn)
- Mild stinging or itching
- Slight swelling
- Skin may peel after a few days
Moderate Burns (Second-Degree)
- Blistering
- Intense pain
- Wet, weeping skin
- White or discolored patches
Severe Burns (Third-Degree)
- Leathery, blackened, or charred skin
- Numbness (nerve damage)
- Difficulty breathing (if inhaled)
- Dizziness or shock
First Aid for Chemical Burns
- 🚿 Rinse Immediately – Flush with cool running water for 20+ minutes.
- 🧤 Remove Contaminated Clothing – Use gloves to avoid further exposure.
- 🧴 Neutralize (If Advised) –
- Acid burns: Diluted baking soda solution
- Alkali burns: Weak vinegar or citrus juice (only after water rinsing)
- 🩹 Cover with Sterile Gauze – Avoid cotton (can stick to wounds).
- 💊 Take Pain Relievers – Ibuprofen or acetaminophen for discomfort.
❌ What NOT to Do:
✖ Apply ice (can worsen tissue damage)
✖ Use butter, oils, or toothpaste (traps chemicals)
✖ Pop blisters (increases infection risk)
Best Chemical Burn Treatment Creams
| Product | Purpose | OTC/Prescription? |
|---|---|---|
| Silver Sulfadiazine | Prevents infection | Prescription |
| Aloe Vera Gel | Soothes & hydrates | OTC |
| Hydrocortisone 1% | Reduces inflammation | OTC |
| Cicalfate (Avene) | Repairs skin barrier | OTC |
| Neosporin | Antibacterial protection | OTC |
Home Remedies for Mild Chemical Burns
- Aloe vera (cooling & healing)
- Honey (antibacterial & soothing)
- Coconut oil (after initial healing)
- Oatmeal baths (for irritation relief)
Avoid:
- Lemon juice (acidic, can worsen burns)
- Essential oils (may irritate damaged skin)
FAQs About Chemical & Acid Burns
1. How long does a chemical burn take to heal?
- Mild burns: 3–7 days
- Moderate burns: 2–3 weeks
- Severe burns: Months (may require skin grafts)
2. Can you put Vaseline on a chemical burn?
✅ Yes, but only after cooling & cleaning (helps lock in moisture).
3. Do chemical burns leave scars?
- Superficial burns: Rarely scar
- Deep burns: High scarring risk (silicone gel helps reduce scars)
4. What’s the difference between acid and alkali burns?
- Acid burns form a hard scab.
- Alkali burns penetrate deeper (more dangerous).
5. Can a chemical burn get infected?
✅ Yes—watch for pus, redness, or fever.