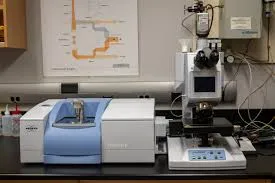
FTIR spectroscopy (Fourier Transform Infrared spectroscopy ) is a powerful analytical technique used to identify organic, polymeric, and some inorganic materials by measuring their absorption of infrared light. Unlike traditional dispersive IR spectrometers, FTIR uses an interferometer for faster, more sensitive measurements.
Table of Contents
What is FTIR Spectroscopy?
Fourier Transform Infrared (FTIR) spectroscopy is the gold standard for molecular identification, analyzing how samples interact with infrared light. Used across industries from pharmaceuticals to environmental science, FTIR provides chemical fingerprints of organic and inorganic materials with minimal sample preparation.
Why Choose FTIR Over Other Techniques?
- 10x faster than dispersive IR spectrometers
- Nanogram-level detection sensitivity
- Non-destructive analysis preserves samples
- Comprehensive databases (20,000+ reference spectra)
How FTIR Spectrometers Work
The FTIR Advantage
Traditional IR spectrometers measure one wavelength at a time. FTIR revolutionized spectroscopy by:
- Using a Michelson interferometer to measure all frequencies simultaneously
- Applying Fourier Transform mathematics to decode complex interference patterns
- Delivering higher signal-to-noise ratios via the multiplex advantage
FTIR Instrument Components
| Component | Purpose | Technical Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| IR Source | Emits broadband infrared | Globar (1500°C SiC), lifetime ~5 years |
| Interferometer | Creates interference | Michelson type, ±0.001 cm⁻¹ accuracy |
| Beam Splitter | Splits IR beam | KBr (4000-400 cm⁻¹), ZnSe (650-450 cm⁻¹) |
| Detector | Measures IR intensity | DTGS (standard), MCT (liquid N₂ cooled) |
| Sample Interface | Holds specimens | ATR, transmission, diffuse reflectance |
Pro Tip: Modern FTIRs like the Thermo Nicolet iS20 feature alignment-free interferometers for maintenance-free operation.
5 Essential FTIR Sampling Techniques
1. Attenuated Total Reflectance (ATR)
Best for: Solids, gels, viscous liquids
✔ No sample prep needed
✔ Surface analysis (~2 µm depth)
✖ Limited to materials with refractive index < crystal
Crystal Materials Comparison
| Material | Range (cm⁻¹) | Chemical Resistance |
|---|---|---|
| Diamond | 4000-400 | Excellent |
| ZnSe | 650-450 | Acid-sensitive |
| Ge | 5500-600 | Alkali-resistant |
2. Transmission FTIR
Best for: Homogeneous liquids, thin films
✔ Highest resolution
✖ Requires precise sample thickness (5-20 µm)
3. Diffuse Reflectance (DRIFTS)
Best for: Powders, rough surfaces
✔ Minimal preparation
✖ Requires Kubelka-Munk transformation
(Continue with Specular Reflectance and Gas Cell techniques…)
FTIR Applications Across Industries
Pharmaceutical Analysis
- Polymorph screening (different crystal forms)
- Counterfeit drug detection (API verification)
- Dissolution testing (formulation stability)
Case Study: Identifying sildenafil citrate in fake Viagra® at 1700 cm⁻¹ (C=O stretch)
Polymer Characterization
- Plastic identification (PE vs. PP)
- Degradation studies (oxidation at 1715 cm⁻¹)
- Additive analysis (phthalates, stabilizers)
Environmental Monitoring
- Microplastics identification in water samples
- Oil spill fingerprinting (petroleum biomarkers)
- Air pollutants (VOCs in gas cells)
Interpreting FTIR Spectra
Characteristic Absorption Bands
| Functional Group | Wavenumber (cm⁻¹) | Peak Shape |
|---|---|---|
| O-H (alcohol) | 3200-3600 | Broad |
| C=O (ketone) | 1715 | Sharp |
| C=C (aromatic) | 1600, 1500 | Doublet |
| NO₂ (explosives) | 1550, 1350 | Strong |
FTIR Maintenance: Keep Your Instrument Peak-Performing
Daily Procedures
- Run background scan with clean ATR crystal
- Verify detector response using polystyrene film
- Check purge gas flow (if applicable)
Monthly Checks
✔ Inspect beam splitter for moisture damage
✔ Clean sample compartment with IPA
✔ Validate wavelength accuracy (polystyrene 1601 cm⁻¹)
Annual Service
- Replace desiccant
- Recalibrate laser alignment
- Source replacement (~10,000 hour lifespan)
FAQs About FTIR Spectroscopy
1. What’s the difference between FTIR and Raman?
FTIR measures absorption of IR light, while Raman detects scattered light. FTIR is better for polar bonds; Raman excels for symmetric vibrations.
2. Can FTIR detect metals?
No – FTIR analyzes molecular vibrations, so elemental metals don’t produce spectra. Use XRF or ICP instead.
3. How much does an FTIR cost?
Prices range from $15,000 for basic models to $100,000+ for research-grade systems with microscopes.
4. What resolution do I need?
- 4 cm⁻¹: Routine QA/QC
- 1 cm⁻¹: Research applications
- 0.5 cm⁻¹: Gas phase analysis
Conclusion: Why FTIR Remains Essential
For over 50 years, FTIR spectroscopy has been the workhorse of molecular analysis because it:
✔ Delivers definitive chemical identification
✔ Requires minimal sample preparation
✔ Adapts to virtually any material state
✔ Provides quantitative and qualitative data