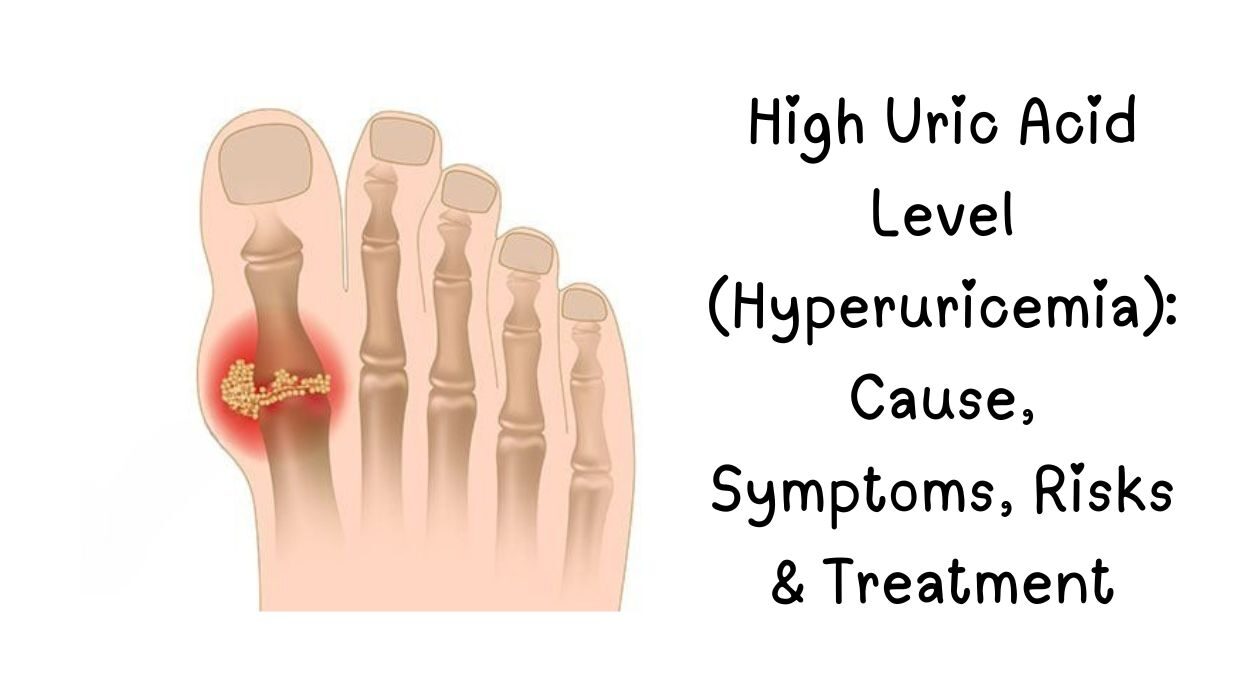
What Is High Uric Acid?
High Uric acid is a natural waste product formed when the body breaks down purines (found in certain foods and cells). Normally, the kidneys filter it out, but when levels get too high, it can cause gout, kidney stones, and joint damage.
How Uric Acid Forms
✔ Purines (from food & dying cells) → Broken down into uric acid → Filtered by kidneys → Excreted in urine.
✔ Problem: If too much is produced or kidneys can’t remove it, levels rise.
Table of Contents
Normal Uric Acid Levels (By Gender)
| Group | Normal Range (mg/dL) | High Risk Level |
|---|---|---|
| Men | 3.4 – 7.0 | > 7.0 |
| Women | 2.4 – 6.0 | > 6.0 |
(Note: Slight variations may occur based on lab standards.)
Signs & Symptoms of High Uric Acid
Many people don’t notice symptoms until complications arise. Watch for:
Gout (Most Common Symptom)
- Sudden, severe joint pain (often in the big toe)
- Redness, swelling, warmth in the affected area
- Attacks lasting 3–10 days
Kidney Stones
- Sharp pain in lower back/side
- Blood in urine
- Frequent, painful urination
Chronic Joint Issues
- Stiffness & limited mobility
- Tophi (uric acid crystal lumps under skin)
What Causes High Uric Acid?
Diet (High-Purine Foods)
- Red meat (beef, lamb)
- Organ meats (liver, kidneys)
- Shellfish (shrimp, crab, mussels)
- Alcohol (especially beer)
Health Conditions
- Obesity (fat cells produce more uric acid)
- Kidney disease (reduces excretion)
- Diabetes & hypertension (linked to higher levels)
Other Factors
- Genetics (family history of gout)
- Dehydration (less urine = more uric acid buildup)
- Medications (diuretics, immunosuppressants)
Related Complications
Left unmanaged, high uric acid can lead to:
Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD)
Crystals can form in the kidneys and damage their filtering capacity over time.
Cardiovascular Issues
Hyperuricemia is associated with high blood pressure, heart attacks, and stroke.
Joint Damage
Repeated gout attacks can lead to permanent joint deformity.
Best & Worst Foods for Uric Acid
| Best Foods (Low Purine) | Worst Foods (High Purine) |
|---|---|
| Cherries (reduce inflammation) | Red meat (beef, pork) |
| Low-fat dairy (yogurt, milk) | Organ meats (liver, kidneys) |
| Citrus fruits (vitamin C helps excretion) | Shellfish (shrimp, crab) |
| Whole grains (oats, brown rice) | Alcohol (especially beer) |
| Vegetables (spinach, kale in moderation) | Sugary drinks & sodas |
(Tip: Lemon water may help alkalize urine and improve excretion.)
Medical Treatments for High Uric Acid
1. Allopurinol
- Reduces uric acid production
- Used for chronic gout prevention
2. Febuxostat (Uloric)
- Alternative for allopurinol intolerance
- More expensive but effective
3. NSAIDs (For Gout Pain)
- Ibuprofen, naproxen reduce swelling & pain
- Colchicine for acute gout attacks
Prevention Tips
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Stay hydrated
- Limit alcohol and sugar
- Get regular health checkups
Natural Ways to Lower Uric Acid
✔ Hydrate well (2–3L water/day flushes kidneys)
✔ Eat cherries (studies show they lower levels)
✔ Limit alcohol & sugar (triggers production)
✔ Exercise regularly (helps with weight control)
✔ Try apple cider vinegar (alkalizing effect)
(Warning: Avoid starvation diets—they can spike uric acid!)
FAQs About Uric Acid
Q: Can high uric acid be cured?
A: No, but it’s manageable with diet, meds, and lifestyle changes.
Q: Does coffee increase uric acid?
A: No! Studies suggest coffee may lower it by improving kidney function.
Q: Are tomatoes bad for uric acid?
A: Debatable. Some gout sufferers report flares, but no strong evidence links them to high levels.
Q: How fast can I lower uric acid?
A: Diet changes show effects in weeks, but meds work faster (days to weeks).
Q: Can stress raise uric acid?
A: Yes! Stress hormones reduce kidney excretion.