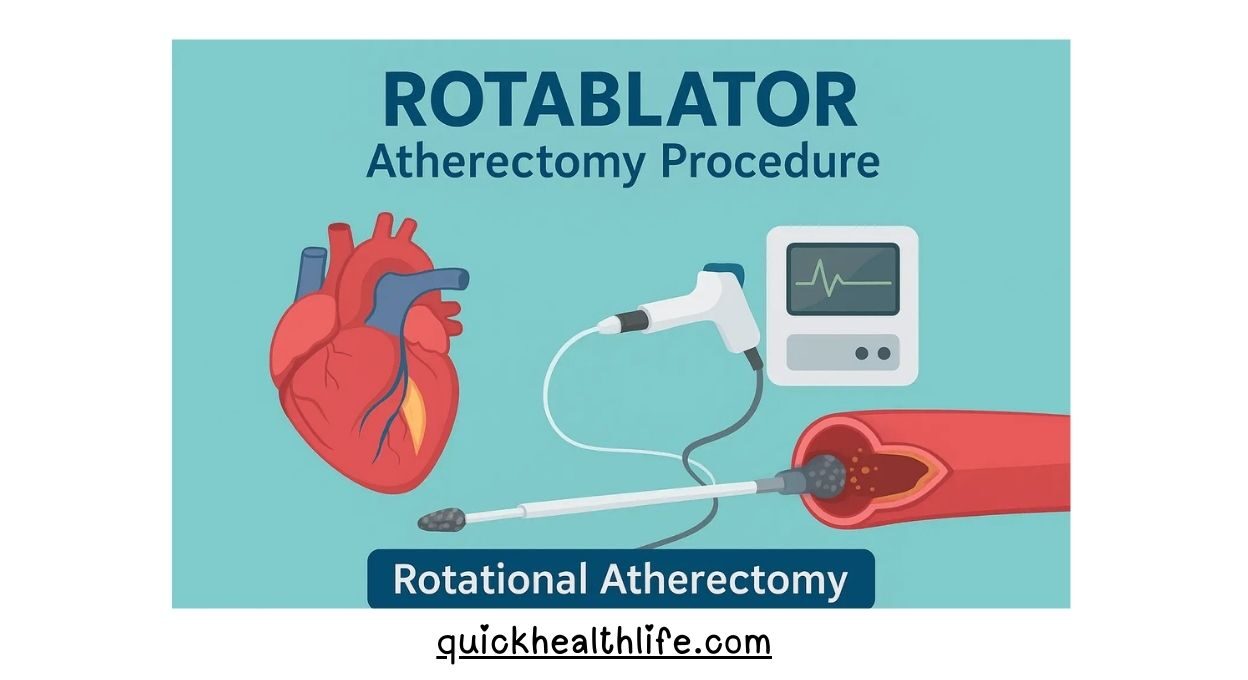
What is a Rotablator Atherectomy Device?
A Rotablator is a medical device used in a special type of angioplasty called Rotational Atherectomy.
- It is mainly used when arteries are blocked with hard, calcified plaque that cannot be treated easily with normal balloon angioplasty.
- The device has a diamond-coated burr that rotates at very high speed to grind the calcium inside arteries into tiny particles.
- These particles are so small that they pass safely into the bloodstream and are removed naturally by the body.
👉 In simple words: A Rotablator is like a tiny drilling machine for heart arteries that clears tough calcium blockages.
Table of Contents
Mechanism of Action of a Rotablator
How does the Rotablator work? Let’s understand step by step:
- A thin wire is passed through the blocked artery.
- The Rotablator burr (diamond-tipped) is attached to a catheter.
- The burr rotates at 140,000 – 200,000 RPM (revolutions per minute).
- It selectively grinds hard plaque without damaging healthy artery tissue.
- After plaque is reduced, a balloon angioplasty or stent placement is performed.
Indications for Rotablation
Rotablation is not for every heart patient. Doctors recommend it when:
- The artery has heavy calcification.
- Normal balloon angioplasty fails to open the blockage.
- The stent cannot pass through the hard blockage.
- There is coronary artery disease (CAD) with complex lesions.
- Elderly patients with long-standing heart blockages.
Types of Atherectomy Devices
There are different atherectomy devices used worldwide:
- Rotational Atherectomy (Rotablator – Boston Scientific)
- Uses a rotating burr.
- Most commonly used worldwide.
- Orbital Atherectomy
- Uses an orbiting crown.
- Works in both directions (forward & backward).
- Directional Atherectomy
- Cuts plaque using a small blade.
- Laser Atherectomy
- Uses laser beams to vaporize plaque.
👉 Among these, the Rotablator (Boston Scientific) is the most widely used device.
Rotablator Procedure Step-by-Step
The rotablation procedure is similar to angioplasty, but with additional steps:
- Preparation – Patient is given local anesthesia & mild sedation.
- Catheter insertion – Through the femoral or radial artery.
- Guidewire placement – A special wire is placed across the blockage.
- Rotablator burr introduced – The diamond-tipped burr is advanced.
- Plaque grinding – Burr rotates at high speed to break calcium.
- Balloon angioplasty/stent – Once plaque is removed, stent is placed.
- Completion – Catheter is removed, and artery opening is restored.
Rotablator Burr Sizes
The burr sizes range between 1.25 mm to 2.5 mm depending on the artery size.
- Smaller burrs for small arteries.
- Larger burrs for bigger arteries with heavy calcium.
👉 Doctors usually start with a smaller burr and increase size gradually if required.
Advantages of Rotablation
- Opens arteries that are impossible to treat with normal angioplasty.
- Improves chances of successful stent placement.
- Reduces complications caused by calcified lesions.
- Helps avoid bypass surgery in some cases.
Risks & Complications of Rotablation
Like any procedure, rotablation has some risks:
- Artery injury or dissection.
- Slow blood flow (no-reflow phenomenon).
- Temporary irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia).
- Rarely, heart attack.
👉 However, in expert hands, success rates are very high.
Rotablation vs Bypass Surgery
| Feature | Rotablation | Bypass Surgery |
|---|---|---|
| Invasiveness | Minimally invasive | Open-heart surgery |
| Recovery time | 2–5 days | 4–6 weeks |
| Risk level | Lower | Higher |
| Suitable for | Calcified arteries not responding to angioplasty | Multiple blockages, severe CAD |
| Cost | Lower | Higher |
👉 Rotablation is often preferred if suitable, but bypass is required for complex, multi-vessel disease.
Rotablator Manufacturers
The main manufacturer of the Rotablator device is Boston Scientific, a leading medical technology company.
Other companies make atherectomy devices, but the Boston Scientific Rotablator is the most trusted and widely used globally.
Rotablator Price & Machine Cost in India
- Rotablator machine price in India: Approx. ₹25 – 40 lakhs depending on hospital and model.
- Rotablator burr (consumable) cost: Around ₹45,000 – ₹90,000 per procedure.
- Procedure cost in India:
- Private hospitals: ₹2.5 – ₹4.5 lakhs
- Government/charity hospitals: ₹1.5 – ₹2.5 lakhs
👉 Cost may vary based on city, hospital, doctor’s expertise, and insurance coverage.
Post-Procedure Care
After rotablation angioplasty:
- Patient stays in hospital for 1–2 days.
- Blood thinners (aspirin, clopidogrel) are prescribed.
- Lifestyle changes: healthy diet, exercise, no smoking.
- Regular follow-up with cardiologist.
Future of Atherectomy Devices
- Newer laser and orbital devices are being developed.
- Research is ongoing to make burrs safer and more effective.
- Combination therapies with drug-eluting stents improve long-term outcomes.
FAQs on Rotablator / Rotablation
Q1. What is rotablator atherectomy?
Ans: It is a procedure where a high-speed rotating burr is used to grind calcium inside blocked arteries, making angioplasty possible.
Q2. What is the cost of rotablator machine?
Ans: In India, it costs between ₹25 – 40 lakhs depending on model and manufacturer.
Q3. What type of devices are used for rotational atherectomy?
Ans: Mainly Rotablator (Boston Scientific), along with orbital, laser, and directional atherectomy devices.
Q4. What is the mechanism of action of a rotablator?
Ans: The burr spins at 140,000–200,000 RPM, grinding hard calcium into microscopic particles.
Q5. Is rotablation better than bypass surgery?
Ans: For single, calcified blockages, rotablation is better. For multiple blockages, bypass may be required.
Q6. Is rotablator available in all hospitals?
Ans: No, it is available only in advanced cardiac centers with trained specialists.
Q7. How long does recovery take after rotablation?
Ans: Usually 2–5 days, much faster than bypass surgery.