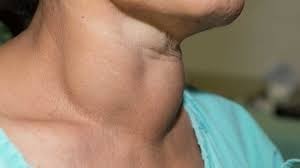
The thyroid is a butterfly-shaped gland located in the front of the neck, below the voice box. It produces hormones that regulate metabolism, growth, and development.
Table of Contents
1. Hypothyroidism (Underactive Thyroid)
Common Causes:
- Hashimoto’s thyroiditis (autoimmune)
- Thyroid surgery/radiation
- Iodine deficiency (rare in developed countries)
- Certain medications (lithium, amiodarone)
Key Symptoms:
☑️ Fatigue and lethargy
☑️ Unexplained weight gain
☑️ Cold intolerance
☑️ Dry skin and hair loss
☑️ Depression/brain fog
☑️ Constipation
First-Line Treatment:
💊 Levothyroxine (Synthroid, Levoxyl, Tirosint) – Synthetic T4
- Typical dose: 1.6 mcg/kg body weight
- Must take on empty stomach (30-60 min before food)
Alternative Options:
💊 Desiccated thyroid (Armour, NP Thyroid) – Contains T4+T3
💊 Liothyronine (Cytomel) – Synthetic T3 (short-acting)
2. Hyperthyroidism (Overactive Thyroid)
Common Causes:
- Graves’ disease (autoimmune)
- Toxic nodules
- Thyroiditis
Key Symptoms:
☑️ Weight loss despite increased appetite
☑️ Rapid/irregular heartbeat
☑️ Heat intolerance
☑️ Tremors/nervousness
☑️ Frequent bowel movements
Treatment Options:
A. Anti-Thyroid Drugs:
💊 Methimazole (Tapazole) – First choice (except 1st trimester pregnancy)
💊 Propylthiouracil (PTU) – Used in pregnancy
B. Definitive Therapies:
☢️ Radioactive Iodine (RAI) – Destroys thyroid tissue
🔪 Thyroidectomy – Surgical removal
3. Thyroid Nodules & Cancer
Evaluation:
- Ultrasound – Checks size/features
- FNA Biopsy – Rules out cancer
- Thyroid Scan – If hyperfunctioning
Cancer Treatments:
- Surgery (total/near-total thyroidectomy)
- Radioactive iodine ablation
- TSH suppression therapy
Monitoring Thyroid Function
Essential Blood Tests:
- TSH (Thyroid Stimulating Hormone)
- Free T4 (Thyroxine)
- Free T3 (Triiodothyronine) – For complex cases
- TPO Antibodies – Diagnoses Hashimoto’s
- TRAb – Diagnoses Graves’ disease
Optimal Ranges (Adults):
- TSH: 0.5-2.5 mIU/L (controversial)
- Free T4: 0.8-1.8 ng/dL
- Free T3: 2.3-4.2 pg/mL
Key Patient Advice
✔️ Take levothyroxine consistently (same time daily)
✔️ Avoid calcium/iron supplements within 4 hours of dose
✔️ Report palpitations, excessive sweating, or persistent fatigue
✔️ Get annual TSH checks if on medication
When to See a Specialist:
- Pregnancy with thyroid disorder
- Unstable TSH levels despite treatment
- Suspected thyroid cancer
- Complex cases (e.g., cardiac issues)
Would you like me to elaborate on any specific aspect of thyroid management?