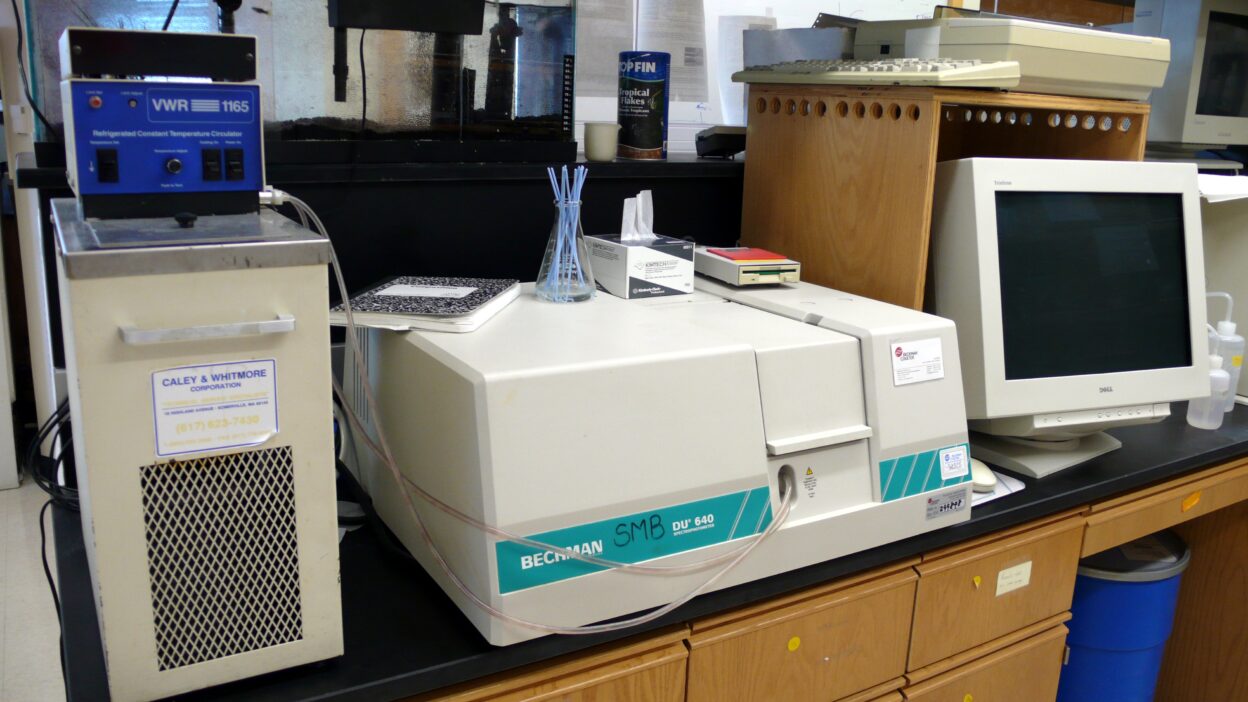
A UV-Vis (Ultraviolet-Visible) Spectrophotometer is an analytical instrument that measures the absorption or transmission of light in the ultraviolet (190–400 nm) and visible (400–700 nm) ranges. It is widely used in chemistry, biochemistry, pharmaceuticals, and environmental testing for quantitative and qualitative analysis.
Table of Contents
1. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Fundamental Components
| Component | Function | Technical Specifications |
|---|---|---|
| Light Source | Emits broadband UV/visible light | – Deuterium lamp (190-400 nm) – Tungsten-halogen (350-1100 nm) – Xenon flash lamps (full range) |
| Monochromator | Wavelength selection | – Czerny-Turner grating (1200-2400 lines/mm) – Bandwidth: 0.1-5 nm |
| Sample Chamber | Holds cuvettes/flow cells | – Path lengths: 1cm (standard), 0.1-10cm options – Temperature control (-10°C to 120°C) |
| Detector | Measures light intensity | – Photomultiplier tubes (PMT, 185-900 nm) – Silicon photodiodes (190-1100 nm) – CCD arrays (for rapid scanning) |
2. UV-Vis Spectrophotometer Parameters
| Parameter | Typical Range | Importance |
|---|---|---|
| Wavelength Range | 190-1100 nm | Determines application scope |
| Spectral Bandwidth | 0.1-5 nm | Affects resolution of sharp peaks |
| Photometric Accuracy | ±0.002-0.5 Abs | Critical for quantitative analysis |
| Stray Light | <0.0001% at 220nm | Impacts low absorbance measurements |
| Scanning Speed | Up to 8000 nm/min | Throughput for kinetic studies |
3. Advanced Instrument Variations
A. Single vs. Double Beam
- Single Beam: Simpler, lower cost (requires reference scan)
- Double Beam: Simultaneous sample/reference measurement (higher stability)
B. Array vs. Scanning
- Diode Array (DAD): Measures all wavelengths simultaneously (fast acquisition)
- Scanning: Higher resolution, better for narrow peaks
4. Sample Measurement Modes
| Mode | Configuration | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Absorbance | Standard mode | Concentration measurements |
| Transmittance | I/I₀ calculation | Filter testing |
| Reflectance | Integrating sphere | Solid/liquid surfaces |
| Kinetic | Time-scan | Enzyme activity studies |
5. Calibration & Validation
Essential Calibration Procedures:
- Wavelength Accuracy: Using holmium oxide (241.15, 287.15, 361.5 nm) or didymium filters
- Photometric Accuracy: NIST-traceable neutral density filters
- Stray Light Check: Potassium chloride (12 g/L) at 200 nm
Daily Validation Tests:
- Baseline flatness (±0.001 AU)
- Noise level (<0.0005 AU peak-peak)
- Repeatability (RSD <0.5%)
6. Cutting-Edge Innovations
- Microvolume Technology: 0.5-2 μL samples (e.g., NanoDrop)
- Fiber Optic Probes: For in-situ measurements
- Hyphenated Systems: HPLC-UV, LC-MS interfaces
- AI Integration: Smart baseline correction algorithms
7. Maintenance Protocols
Monthly:
- Lamp alignment check
- Cuvette holder cleaning
- Wavelength calibration verification
Annual:
- Source replacement (1000-2000 hr lifespan)
- Full optical path alignment
- Detector sensitivity test
8. Common Applications with Typical Parameters
| Application | Wavelength | Sample Type | Accuracy Required |
|---|---|---|---|
| DNA Quantification | 260 nm | Aqueous solution | ±2 ng/μL |
| Protein Assay (Bradford) | 595 nm | Colored complex | ±0.1 mg/mL |
| Pharmaceutical Purity | Varies | Tablet extracts | ±0.5% label claim |
| Water Quality (NO₃⁻) | 220/275 nm | Filtered water | ±0.05 ppm |
9. Troubleshooting Guide
| Issue | Possible Causes | Solutions |
|---|---|---|
| Noisy baseline | Lamp aging, dirty optics | Replace lamp, clean cuvette holder |
| Wavelength shift | Grating misalignment | Perform wavelength calibration |
| Negative absorbance | Improper blanking | Re-zero with fresh blank |
| Non-linear response | Stray light, detector saturation | Check calibration, dilute sample |
Modern instruments like Agilent Cary 60 or Shimadzu UV-2600 now feature:
- Touchscreen interfaces with method wizards
- Built-in regulatory compliance (21 CFR Part 11)
- Cloud connectivity for data management
- Automated cell changers for high-throughput