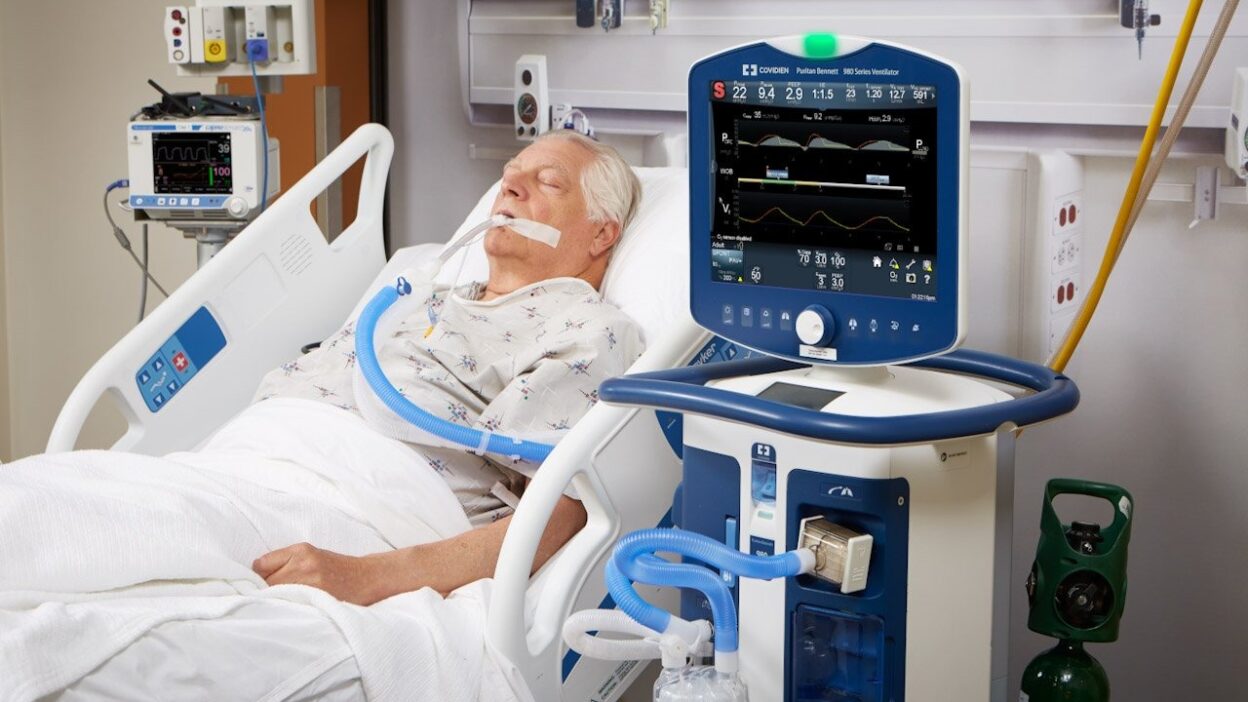
When lungs fail, mechanical ventilators become critical life support. These machines breathe for you during surgeries, severe infections like COVID-19, or traumatic injuries. Unlike oxygen masks, ventilators actively push air into your lungs while removing carbon dioxide – a complex intervention used in 30-50% of ICU patients.
Table of Contents
How Ventilators Work
Ventilators use positive pressure to force oxygen into your airways. Here’s the process:
- Air Intake: Machine pulls in filtered room air
- Oxygen Mixing: Blends pure oxygen to prescribed concentration (21-100%)
- Delivery: Pushes air through tubes into lungs
- Expiration: Allows passive exhalation via release valve
- Monitoring: Sensors track oxygen/carbon dioxide levels 24/7
| Setting | Typical Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Tidal Volume | 6-8 mL/kg | Prevents lung overstretch |
| Respiratory Rate | 12-20 breaths/min | Maintains CO2 balance |
| FiO₂ | 30-60% | Oxygen concentration delivered |
| PEEP | 5-15 cm H₂O | Keeps alveoli open between breaths |
Invasive vs. Non-Invasive Ventilation
Invasive Mechanical Ventilation
- Used For: Unconscious patients, severe ARDS, major surgery
- Access: Endotracheal tube (mouth) or tracheostomy (neck)
- Pros: Full breathing control, airway protection
- Cons: Infection risk, requires sedation
Non-Invasive Ventilation (NIV)
- Used For: COPD exacerbations, sleep apnea, post-extubation support
- Devices: CPAP/BiPAP masks, helmet interfaces
- Pros: Preserves speech/swallowing, lower infection risk
- Cons: Limited pressure support, not for coma patients
Who Needs Ventilators? Critical Conditions
| Condition | Ventilation Type | Average Duration |
|---|---|---|
| Pneumonia/COVID-19 | Invasive | 7-14 days |
| COPD Exacerbation | Non-Invasive (BiPAP) | 3-5 days |
| General Anesthesia | Invasive (temporary) | Hours |
| Traumatic Brain Injury | Invasive | Weeks-months |
| Spinal Cord Injury | Invasive + tracheostomy | Years |
Top 5 Emergency Triggers:
- Oxygen saturation <90% despite high-flow oxygen
- Respiratory rate >35 breaths/min
- Unconsciousness with airway obstruction
- Acute hypercapnia (PaCO₂ >50 mmHg)
- Severe asthma attack unresponsive to drugs
Risks vs Benefits: The Critical Balance
Benefits
✅ Maintains oxygen during lung healing
✅ Reduces breathing workload by 100%
✅ Prevents lung collapse with PEEP
✅ Buys time for antibiotics/steroids to work
Risks
❌ Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia (10-20% of cases)
❌ Barotrauma: Lung tears from pressure (5% risk)
❌ Ventilator Dependence: Muscle atrophy after 2+ weeks
❌ Delirium: 70% of patients experience ICU psychosis
The Ventilator Timeline: From Intubation to Weaning
- Day 1-3: Deep sedation, full ventilator control
- Day 4-7: Daily “spontaneous breathing trials” (SBTs)
- Success Criteria: Maintains oxygen with minimal support
- Weaning: Gradual reduction of ventilator settings
- Extubation: Tube removal when:
- Cough/gag reflex present
- Oxygen >92% on FiO₂<40%
- Passing SBT for 30+ min
Alarming Stat: 15% of patients require re-intubation within 48 hours (Chest Journal).
ICU Care Team: Who Manages Your Ventilation?
| Role | Responsibilities |
|---|---|
| Intensivist | Oversees ventilator settings & weaning |
| Respiratory Therapist | Adjusts machine, performs suctioning |
| ICU Nurse | Monitors vitals, administers sedation |
| Pulmonologist | Manages lung disease complications |
| Speech Therapist | Assesses swallowing post-extubation |
Post-Ventilator Recovery: What to Expect
- Day 1: Hoarse voice, sore throat, weak cough
- Week 1: Physical therapy for muscle rebuilding
- Month 1: Pulmonary rehab for lung strengthening
- Long-Term: Possible PTSD, vocal changes, tracheostomy scars
3 Must-Do Rehab Exercises:
- Incentive spirometry: 10 breaths/hour while awake
- Diaphragmatic breathing: 5 min hourly
- Walking: 5-min increments 4x daily
PEEP vs CPAP Work
| Feature | PEEP | CPAP |
|---|---|---|
| Use Case | Ventilated ICU patients | Sleep apnea/home COPD care |
| Pressure Type | End-expiratory only | Continuous (in/out phases) |
| Oxygen Boost | +15-25% oxygenation | +10-20% oxygenation |
| Risks | Pneumothorax, low BP | Mask discomfort, dry mouth |
FAQs About Ventilator
Q1: Can you feel the ventilator breathing for you?
A: Sedated patients feel nothing. Awake patients describe pressure sensations but no pain.
Q2: How long before ventilator dependence starts?
A: Diaphragm weakening begins at 7 days. Tracheostomy considered at 14 days.
Q3: Why do vent patients need restraints?
A: Prevents accidental tube removal – a life-threatening emergency.
Q4: Can you talk on a ventilator?
A: Only with specialized “talking tracheostomy” tubes. Standard tubes block speech.
Q5: What’s the survival rate for ventilated patients?
A: Varies by condition:
- Pneumonia: 65%
- ARDS: 50%
- Cardiac arrest: 30%
Q6: Do ventilators treat COVID-19?
A: No – they support breathing while antivirals/immune therapies work.
Q7: How is nutrition given?
A: Through nasogastric tubes (nose to stomach) with liquid formulas.
Q8: Can ventilators cause brain damage?
A: No – but oxygen deprivation before ventilation can.
Q9: What’s the “ventilator bundle”?
A: 4 safety protocols:
- Head elevation 30°
- Daily sedation breaks
- Ulcer prevention meds
- Blood clot prophylaxis
Q10: When is ventilation withdrawn?
A: When treatment is futile – guided by advance directives/family consensus.
Q11: Can children use adult ventilators?
A: Never – pediatric vents have smaller tidal volumes and specialized alarms.
Q12: Home ventilation costs?
A: $1,500-$4,000/month for portable BiPAP/ventilator systems.